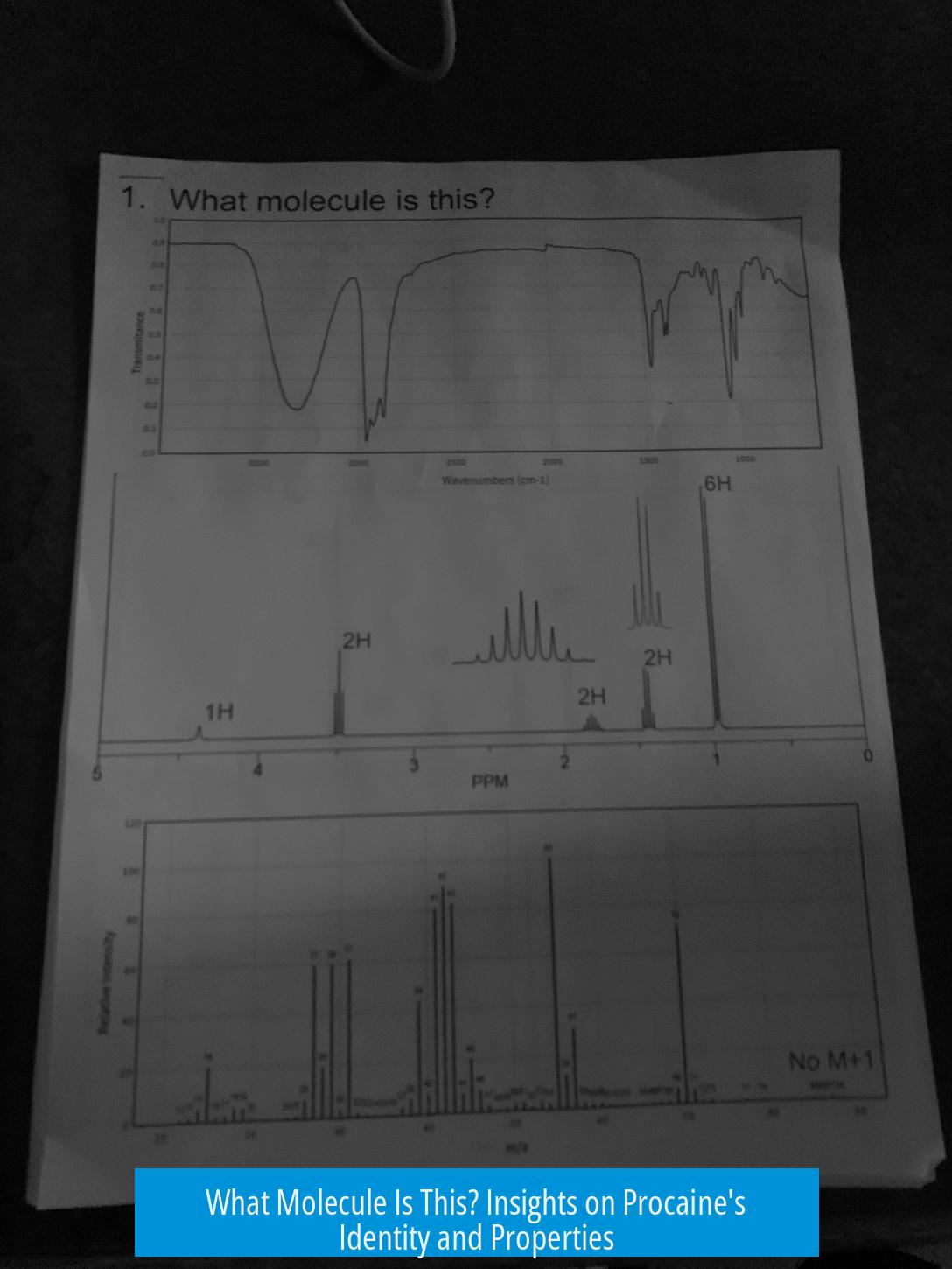
What molecule is this? Understanding Procaine
The molecule in question is Procaine, also known by its chemical name 2-(N,N-diethylamino)ethyl 4-aminobenzoate. It is a synthetic compound widely recognized as a local anesthetic used in medical procedures to numb tissue in specific areas.
Chemical Identity of Procaine
- Chemical Structure: Procaine consists of an amino ester linkage between a diethylaminoethyl group and 4-aminobenzoic acid.
- Synonyms: It is commonly called Novocaine, a term often used in dental anesthesia.
- Molecular Composition: The molecule includes terminal methyl groups and functional groups responsible for its anesthetic effect.
Pharmacological Properties
Procaine acts as a local anesthetic by blocking nerve signal transmission. This effect temporarily numbs the targeted area without affecting consciousness.
It is mainly used in minor surgical and dental procedures to reduce pain sensitivity. Compared to other anesthetics, procaine has a short duration of action and minimal systemic toxicity.
Relation to Cocaine
- Procaine shares a similar anesthetic effect with cocaine but lacks its powerful central nervous system stimulant properties.
- Historically, it has been used to dilute cocaine illicitly, due to its similar numbness sensation and lower cost.
- This resemblance has led to cultural references where procaine is called “the cocaine of professionals.”
Additional Insights
The word molecule originates from the Latin “molecula,” meaning “little mass” or “small lump,” highlighting the fundamental nature of such chemical entities.
Procaine’s distinct structure and purpose make it a key example in teaching organic and medicinal chemistry.
Key Takeaways
- Procaine is a local anesthetic with the chemical name 2-(N,N-diethylamino)ethyl 4-aminobenzoate.
- It blocks nerve signals to numb areas during minor surgeries and dental work.
- Procaine has structural similarities to cocaine but lacks stimulant effects.
- It is sometimes illicitly used to adulterate cocaine due to its similar anesthetic properties.
- The molecule exemplifies key concepts in chemistry and pharmacology.
What is the chemical name of the molecule called Procaine?
Procaine is chemically known as 2-(N,N-diethylamino)ethyl 4-aminobenzoate. It is also commonly called Novocaine.
What is Procaine mainly used for?
Procaine is primarily used as a local anesthetic. It numbs tissue in a specific area to reduce pain during medical procedures.
How is Procaine related to cocaine?
Procaine is often compared to cocaine as both are anesthetics. Historically, procaine has been used as a less potent substitute or adulterant in cocaine.
Why is Procaine sometimes called “the cocaine of professionals”?
This nickname highlights procaine’s use as a safe alternative to cocaine in medical settings. It lacks cocaine’s addictive properties but still numbs effectively.
What is the significance of the name “molecule” mentioned in the content?
The term molecule comes from the Latin for “little lumps,” reflecting small particles that make up substances like Procaine.




Leave a Comment