What Are Molecular Compounds?
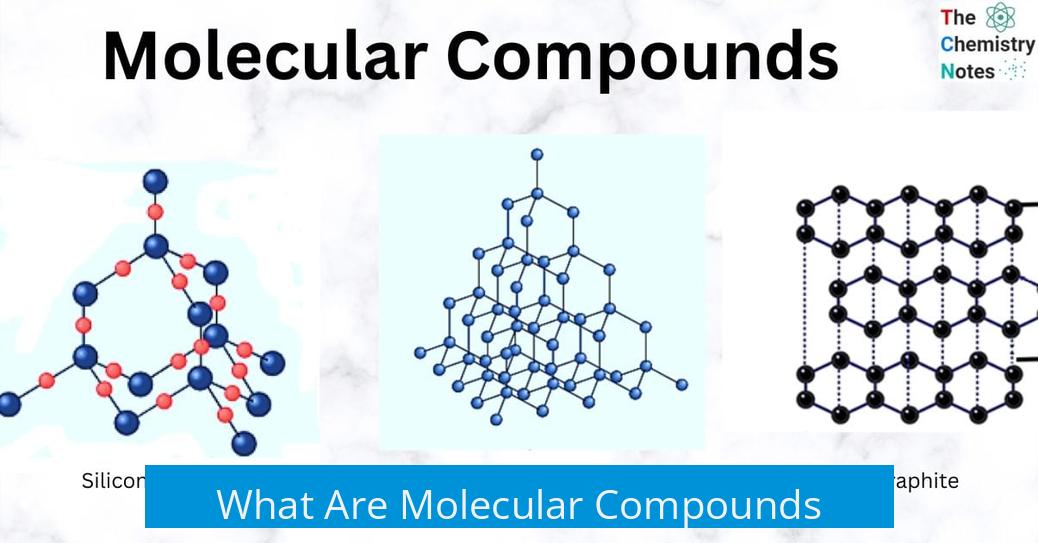
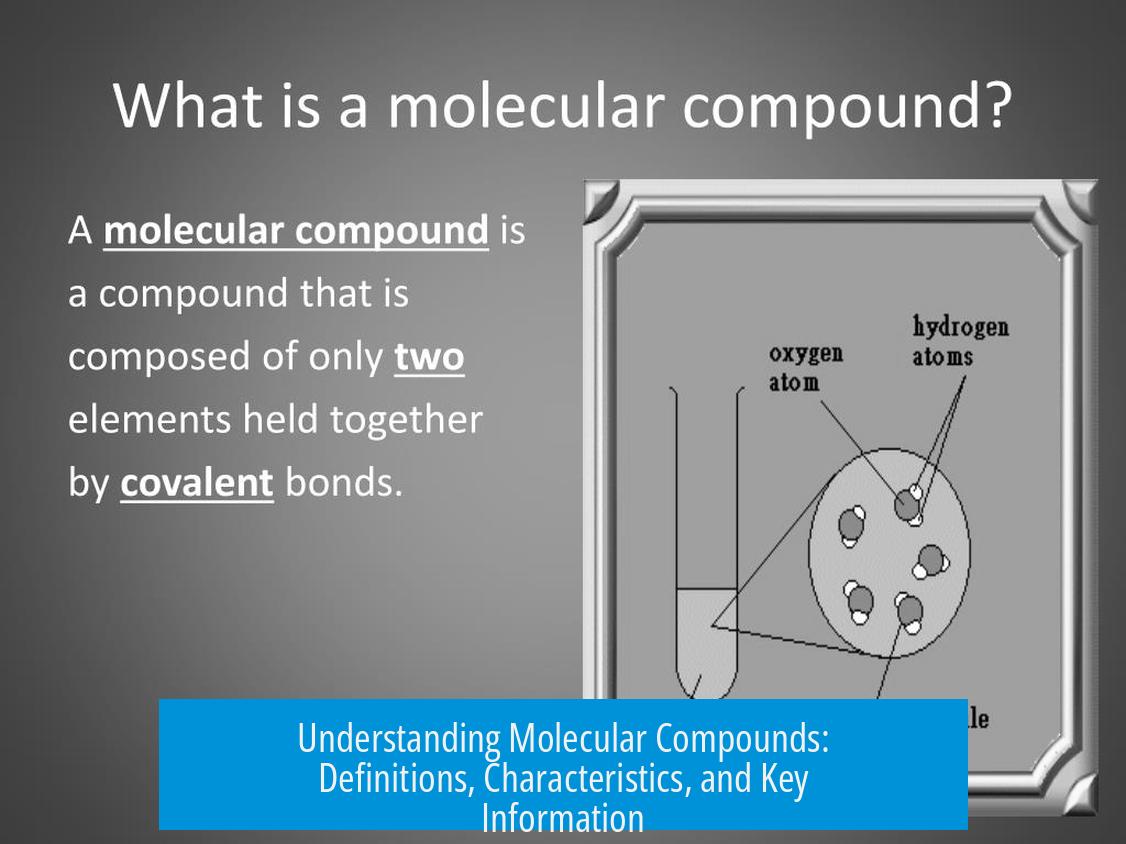
Molecular compounds consist of two or more atoms covalently bonded together, forming discrete units called molecules. These atoms can be of the same or different elements. Molecular compounds are often synonymous with covalent compounds, and these terms are used interchangeably in chemistry.
Terminology and Naming

The terms molecule, molecular compound, and covalent compound largely overlap. Chemists introduced different names to create parallels with ionic compounds and to clarify naming conventions. For instance, calling them “covalent compounds” aligns structurally with ionic compounds in textbooks and helps students link bonding types with compound names.
Distinctions between these terms rarely matter in practical chemistry; most professionals treat them synonymously. Exceptions are exceedingly rare and mostly concern nuanced linguistic preferences rather than chemical differences.
Definition and Characteristics
- Molecular compounds form when atoms share electrons via covalent bonds.
- Molecules have a definite number of atoms arranged in a specific order.
- Compounds with larger carbon-containing structures, typical in organic chemistry, are often called molecular compounds.
- Smaller compounds without carbon or with few carbons can also be termed covalent compounds.
These molecules interact through intermolecular forces, which influence their physical properties.
Variations and Exceptions
Most molecular compounds are distinct molecules with clear boundaries. However, some covalent compounds form extended network solids, like quartz (SiO2), where covalent bonds extend throughout the structure rather than forming separate molecules.
Some molecular substances may not feature purely covalent bonds. For example, noble gases and benzene-ion complexes show deviations due to unique bonding or interactions, making the classification less strict in those cases.
Summary
In essence, molecular compounds are stable entities formed by two or more atoms joined through shared electrons. They are distinguished from ionic compounds by the nature of their bonding. This grouping plays a crucial role in the study of chemistry due to their diverse properties and wide occurrence.
Key Takeaways
- Molecular compounds are composed of atoms covalently bonded into fixed structures called molecules.
- Terms like molecule, molecular compound, and covalent compound are generally interchangeable.
- They contrast with ionic compounds that rely on ionic bonds between ions.
- Exceptions include covalent network solids and some unique molecular entities lacking standard covalent bonding.
- Understanding molecular compounds helps explain a large variety of chemical substances, especially in organic chemistry.




Leave a Comment