Understanding Anomers in Simple Terms
An anomer is a specific type of diastereomer that differs in configuration at only one carbon atom, called the anomeric carbon. This concept primarily applies to sugar molecules and helps explain their structural variations.
What Is an Anomer?
To grasp anomers, it helps to understand diastereomers. Diastereomers are molecules that have the same formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms in space. Anomers belong to this category but differ only in the 3D arrangement around a single carbon atom.
This unique carbon is called the anomeric carbon.
The Anomeric Carbon in Sugars
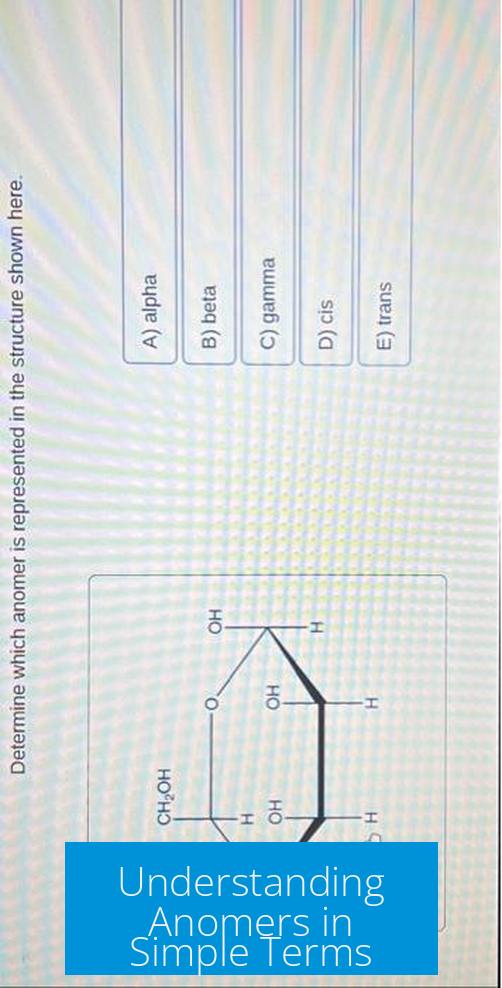
In sugar chemistry, the anomeric carbon is usually carbon number 1. For glucose, this carbon is located between an internal oxygen atom and an -OH group. This carbon forms part of a hemiacetal group.
This carbon is crucial because it can adopt different spatial arrangements, leading to distinct forms of the sugar.
The Two Types of Anomers
- Alpha (α) anomer: The -OH group on the anomeric carbon is positioned on the opposite side of the ring relative to the CH2OH group.
- Beta (β) anomer: The -OH group on the anomeric carbon is on the same side as the CH2OH group.
Both alpha and beta anomers are chemically similar, but their difference in spatial arrangement affects how they interact with enzymes and other molecules.
Why Are Anomers Important?
Anomers influence the properties of sugars, including sweetness, solubility, and how they are metabolized. Some enzymes specifically recognize one anomer over the other.
This subtle difference plays a vital role in biochemistry and food science.
Key Takeaways
- An anomer is a type of sugar molecule differing in configuration at the anomeric carbon.
- The anomeric carbon is carbon 1 in sugars like glucose and forms a hemiacetal.
- There are two anomers: alpha (α) and beta (β), differing in the position of the -OH group.
- Anomers affect sugar properties and biological interactions.
What exactly is an anomer?
An anomer is a type of molecule called a diastereomer. It is different because it changes only at one specific carbon atom in the molecule.
Where is the anomeric carbon located in sugars?
The anomeric carbon is the first carbon in sugar molecules. In glucose, it sits between an oxygen inside the ring and an OH group.
How many types of anomers exist?
Two types of anomers exist: alpha and beta. The only difference is how the groups are arranged around the anomeric carbon.
Why are anomers important in sugar chemistry?
Anomers show how sugar molecules can differ in 3D shape. This small change affects how they react and taste.
How do anomers relate to diastereomers?
Anomers are a special kind of diastereomer. They differ only at the anomeric carbon, while other diastereomers can differ at multiple places.




Leave a Comment