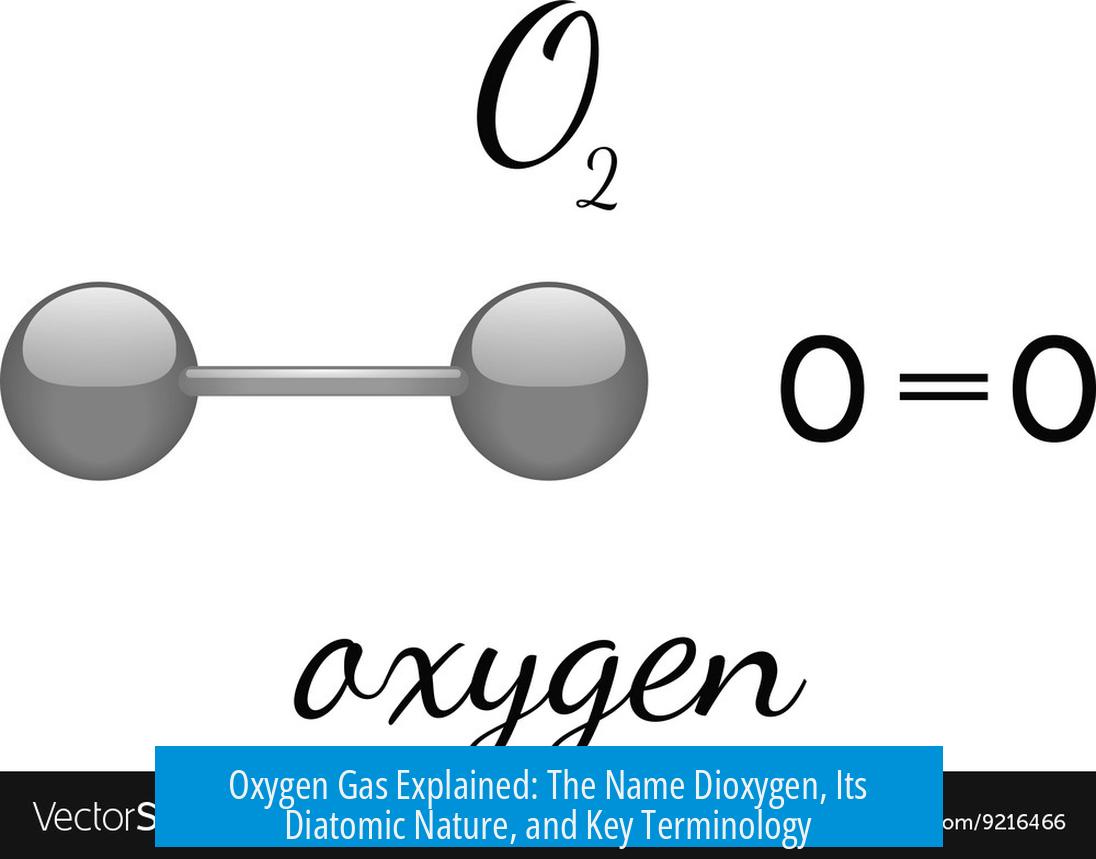
Understanding O2: Oxygen Gas and Its Naming

O2 refers to oxygen gas, which is a diatomic molecule composed of two oxygen atoms bonded together. This form of oxygen exists naturally and is the most common elemental form found in Earth’s atmosphere. Often, people simply call it “oxygen gas” since it is the prevalent gaseous form of oxygen.
Diatomic Nature of Oxygen

Oxygen atoms rarely exist alone under normal conditions. Instead, two oxygen atoms join to form O2. This pairing creates a stable molecule essential for life and combustion processes. The diatomic structure explains many physical and chemical properties of oxygen gas.
Why the Name “Dioxygen” Instead of “Dioxide”?
- Oxide vs Dioxygen: The term “oxide” generally refers to the O2− ion, an oxygen atom carrying a negative charge in ionic compounds.
- Dioxygen: Since O2 is a neutral molecule with no net charge, it is more accurate to call it “dioxygen,” which highlights the presence of two oxygen atoms without implying ionic charge.
- Dioxide Usage: “Dioxide” typically applies to compounds where oxygen is bonded ionically or covalently with another element—such as carbon dioxide (CO2)—not to elemental oxygen gas.
- For example, fluorine gas (F2) is not called “difluoride gas” even though it contains two fluorine atoms.
Common Terminology
Often, “oxygen gas” suffices when discussing O2, especially in everyday or scientific communication. The clarity about its diatomic form simplifies understanding. In contexts involving chemical reactions or atmospheric studies, knowing the diatomic nature helps explain oxygen’s behavior.
Summary of Key Points
- O2 is the molecular form of oxygen gas, consisting of two oxygen atoms.
- It is called dioxygen rather than dioxide because it is a neutral molecule, not an ion.
- “Dioxide” refers to oxygen-containing compounds with another element, not pure oxygen gas.
- Oxygen’s diatomic nature underpins its chemical and physical properties.
- “Oxygen gas” is a standard term for O2 in most contexts.
What does the term “dioxygen” mean in relation to O2?
“Dioxygen” refers to the O2 molecule, which is two oxygen atoms bonded together. It emphasizes that O2 is a neutral molecule, not an ion.
Why is O2 called dioxygen instead of dioxide?
O2 is neutral, so it’s dioxygen. “Dioxide” implies an ionic compound, usually involving O(2-) ions. O2 does not carry a charge, so “dioxide” is not accurate here.
Is oxygen always found as O2 gas?
Oxygen mostly exists as O2 gas, its common and stable form. This diatomic gas is what we breathe and see in everyday air.
Why don’t we say “difluoride gas” for fluorine gas?
The name follows chemical naming rules. Like oxygen, fluorine gas consists of two atoms, but the term “difluoride” is reserved for ionic compounds, not the neutral F2 molecule.



Leave a Comment