Did you know that the number of electrons in an atom is the key to understanding how elements interact with each other on a molecular level? This knowledge is essential for anyone who wants to explore the world of chemistry. But how do you find the number of electrons in an atom?
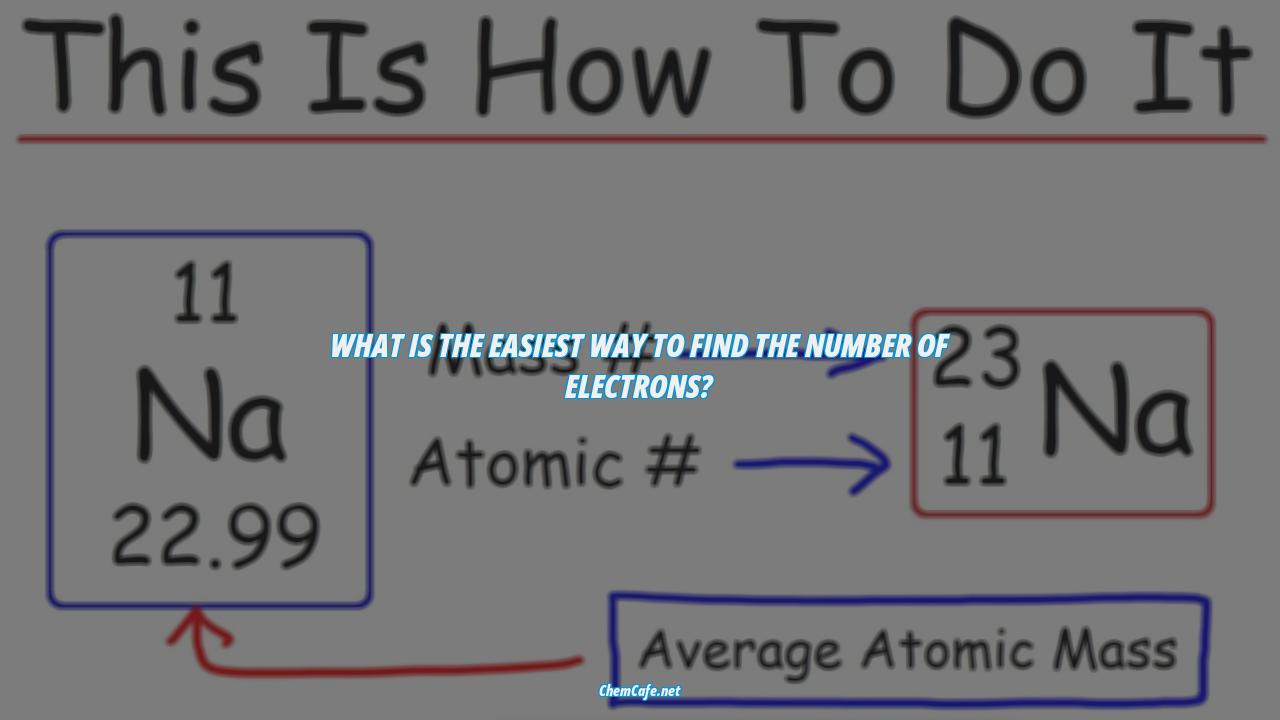
The answer is surprisingly simple. All you have to do is look up the element you’re working with on the periodic table and locate its atomic number. This will be in the upper left-hand corner of the square. Once you have that number, it’s easy to determine the number of electrons.
But what if the atom has a charge? Not to worry. You can still easily figure out the number of electrons. All you have to do is identify the charge of the ion, which will be written as a superscript to the right of the element. Then you just subtract the number of protons from the number of electrons to get the total number of electrons.
The atomic number is also the number of protons in an atom. This means that the number of protons is equal to the atomic number of the element. So let’s say you want to figure out the number of electrons in an oxygen atom. All you have to do is look up the periodic table and locate the element’s atomic number (eight).
To determine the number of electrons from the proton number, you need to identify the charge of the ion. It should be written as a superscript to the right of the element. Then subtract the number of protons from the number of electrons to get the total number of electrons.
Finally, if you want to explore the electron configuration of an element, you can count the electrons in a molecule by identifying the bonds between the atoms. This will help you determine the type of bond, as well as the number of electrons in the molecule.
So there you have it! With just a few simple steps, you can easily determine the number of electrons in an atom. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be ready to tackle any chemistry problem that comes your way.
What is the easiest way to find the number of electrons?
Finding the number of electrons in an atom can be tricky, but there are a few key steps to follow that make it easier. Knowing the number of electrons is important for understanding how atoms interact with each other and how chemical reactions work. In this article, we’ll discuss the easiest way to find the number of electrons in an atom.
Finding the Atomic Number
The easiest way to find the atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom, is to look on a periodic table. The atomic number is in the upper left corner, or is the largest number on the square. For example, if you’re looking for the atomic number of oxygen, it’s 8.
Finding the Number of Protons
The number of protons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. For example, let’s use oxygen. According to the periodic table, oxygen has the atomic number eight. The atomic number is located above the element’s symbol.
How to Determine the Number of Electrons
Once you know the atomic number and the charge of the ion, you can easily calculate the number of electrons. The number of electrons is equal to the atomic number minus the charge of the ion. For example, if an element has an atomic number of 8 and a charge of +2, then it has 6 electrons.
Other Ways to Find the Number of Electrons
There are a few other ways to find the number of electrons in an atom. For example, if you know the element’s electron configuration, you can count the number of electrons in each orbital. You can also calculate the number of electrons from the element’s mass number, which is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Finding the number of electrons in an atom is important for understanding how atoms interact with each other and how different chemical reactions work. The easiest way to find the number of electrons in an atom is to look up the element on the periodic table and locate its atomic number. Then, identify the charge of the ion, which will be written as a superscript to the right of the element. Finally, calculate the number of electrons by subtracting the charge of the ion from the atomic number.
If you need more help understanding how to find the number of electrons in an atom, consider working with a tutor or taking an online course. With the right resources and guidance, you can quickly master the basics of atomic structure and learn how to find the number of electrons in any atom.
How do you find the total number of electrons?
The number of electrons in an atom is determined by its atomic number. This number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It is an important piece of information for understanding the structure and behavior of an atom, and it is essential for determining the number of electrons.
Step 1: Look Up The Element’s Atomic Number
The first step to finding the total number of electrons is to look up the element’s atomic number. This number is found in the upper left-hand corner of the square for each element on the periodic table. For example, the atomic number of Potassium is 19, Nitrogen is 7, Oxygen is 8 and Sulfur is 16.
Step 2: Find Out The Number Of Atoms Of Each Element
The next step is to find out the number of atoms of each element in the molecule. This can be done by counting the number of atoms in a molecule or by using a molecular formula. For example, the molecular formula of water is H2O, which means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in a molecule of water.
Step 3: Calculate The Number Of Electrons
Once you have the atomic number and the number of atoms of each element, you can calculate the total number of electrons. This calculation is done by multiplying the atomic number of each element by the number of atoms of that element.
For example, if you have two molecules of water, the total number of electrons would be:
(2 x 19) + (2 x 7) + (2 x 8) + (2 x 16) = 116
Step 4: Find The Number Of Protons
The number of protons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. To find the number of protons, you simply need to look up the atomic number of the element on the periodic table. For example, the atomic number of oxygen is 8, so oxygen has 8 protons.
Finding the total number of electrons in an atom is a simple process. Start by looking up the element’s atomic number, then find out the number of atoms of each element in the molecule. Finally, multiply the atomic number of each element by the number of atoms of that element to calculate the total number of electrons.
How do you find the number of electrons?
Finding the number of electrons an atom contains is an important step in understanding its behavior. Electrons are responsible for chemical bonding, so it is important to know how many electrons an atom has in order to understand how it will interact with other atoms.
In this article, we will discuss the easy ways to find the number of electrons in an atom, as well as how to determine the number of electrons from the proton number.
Finding the Number of Protons
The number of protons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. For example, let’s use oxygen. According to the periodic table, oxygen has the atomic number eight. The atomic number is located above the element’s symbol.
Knowing the number of protons in an atom is helpful in determining the number of electrons. To do this, we need to know the mass number of the element. The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in an element.
Determining the Number of Neutrons
Once we have the mass number and the atomic number, we can determine the number of neutrons in an atom. This is done by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. For example, if the element has a mass number of 23 and an atomic number of 11, then the number of neutrons is 12 (23 – 11 = 12).
Determining the Number of Electrons
The number of electrons in an element can change. For a neutral atom, the number of protons is exactly equal to the number of electrons. So the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number. However, it is possible to remove electrons and not change the identity of an element. These are called ions.
How to Determine the Number of Electrons from the Proton Number
There is an easy way to determine the number of electrons from the proton number. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Identify the proton number, also called atomic number, of the element on the periodic table of elements.
Step 2: If it is an ion, determine the charge of the ion. This can be seen in the name of the ion.
Step 3: If it is a neutral atom, then the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number. If it is an ion, the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number plus or minus the charge of the ion.
For example, if the element has an atomic number of 6 and it is a negative ion, then the number of electrons is 4 (6 – 2 = 4).
Understanding the number of electrons an atom contains is an important part of understanding its behavior and its ability to form chemical bonds. Knowing the atomic number and mass number of an element allows us to easily calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. We can also determine the number of electrons from the proton number, by taking into account the charge of the ion.
How do you find the number of electrons without a charge?
The number of electrons an atom has is an important factor in determining its chemical properties. Fortunately, you can find the number of electrons without a charge by following a few simple steps. In this blog, we’ll explain how to determine the number of electrons without a charge.
Step 1: Look up the element
The first step to finding the number of electrons without a charge is to look up the element you’re working with on the periodic table. The atomic number of the element will be in the upper left-hand corner of the square. Make sure to write down the atomic number, as you’ll need it in the next step.
Step 2: Identify the charge of the ion
The next step is to identify the charge of the ion. This will be written as a superscript to the right of the element. If the charge is positive, it will be written as a “+” sign. If the charge is negative, it will be written as a “-” sign.
Step 3: Determine the number of electrons
Now that you know the atomic number of the element and the charge of the ion, you can determine the number of electrons. If it is a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the proton number. If the ion is positively charged, the number of electrons is found by subtracting the charge number from the proton number. If the ion is negatively charged, the number of electrons is found by adding the charge number to the proton number.
Finding the number of electrons without a charge can be a tricky process. However, if you follow the steps outlined above, you should have no trouble determining the number of electrons. Remember to look up the element on the periodic table and identify the charge of the ion before calculating the number of electrons. Good luck!
What is the easiest way to find the electron configuration of an element?
Electron configurations are an essential tool used by chemists and physicists to understand the properties of elements. Knowing the electron configuration of an element can help us determine its valency, predict the properties of a group of elements, and interpret atomic spectra. But how do we determine the electron configuration of an element?
What are Electron Configurations?
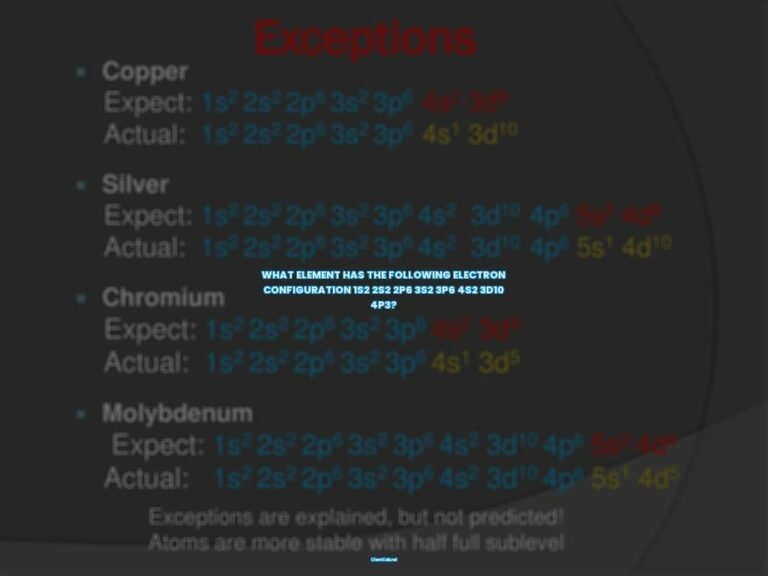
Electron configurations describe how electrons are distributed in the atomic orbitals of an element. They are typically written in a standard notation, with all electron-containing atomic subshells listed in a sequence and the number of electrons they hold written in superscript. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1.
The conventional way to determine electron configuration
In a neutral element, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons it has. This means that the orbitals of an element must be filled with electrons in order for it to be stable. The number of orbitals an element has depends on its atomic number, and the more electrons it has, the more orbitals it will have to fill.
Electron configurations are typically written using a notation which lists the orbital symbols sequentially, with a superscript indicating the number of electrons occupying that orbital. This notation is useful for indicating the distribution of electrons among available orbitals, but it can become quite lengthy for elements with a larger atomic number.
The easiest way to find electron configuration
The easiest way to find the electron configuration of an element is to use a periodic table. Most periodic tables come with the electron configuration of each element written in a simplified form, so all you have to do is look up the element you need and copy the configuration.
However, if you want to determine the electron configuration of an element yourself, you can use the Aufbau Principle. This principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy level, starting with the lowest energy level and moving up.
Electron configurations are essential for understanding the properties of elements. The standard notation for writing electron configurations can become quite lengthy, but the easiest way to find the electron configuration of an element is to use a periodic table or the Aufbau Principle. With this information in hand, chemists and physicists can make more informed predictions about the behavior of elements.
How do you count electrons in a molecule?
Electrons play an important role in the formation of molecules. They are responsible for the chemical bonds that hold atoms together, and they are also responsible for the properties of the molecules they form. Knowing how to count electrons in a molecule is essential for understanding the chemical properties of a material, as well as for designing chemical reactions.
Step 1: Find the Atomic Number of each Element
The first step in calculating the number of electrons in a molecule is to find the atomic number of each element that is involved. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, and it is listed on the periodic table of elements. For example, the atomic number of oxygen is 8.
Step 2: Determine the Number of Electrons per Atom
The second step in calculating the number of electrons in a molecule is to determine the number of electrons per atom. This can be done by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight of the element. For example, the atomic weight of oxygen is 16, so the number of electrons per atom would be 8 (16-8 = 8).
Step 3: Calculate the Total Number of Electrons
Once you have the number of electrons per atom, you can calculate the total number of electrons by multiplying the number of atoms of each element by the number of electrons per atom. For example, if you have a molecule with two oxygen atoms, the total number of electrons would be 16 (2 x 8 = 16).
Step 4: Add Electrons from Chemical Bonds
Atoms form molecules and compounds by sharing electrons to create chemical bonds. These bonds are represented by a pair of electrons, or “lone pairs.” To determine the number of electrons from chemical bonds, count the number of bonds in the molecule. For example, if a molecule has two bonds, the total number of electrons from bonds would be 4 (2 x 2 = 4).
Step 5: Calculate the Total Number of Electrons in the Molecule
Finally, add this value to the total from Step 3 to determine the total number of electrons in the molecule. For example, if the total number of electrons from Step 3 was 16 and the total number of electrons from chemical bonds was 4, the total number of electrons in the molecule would be 20 (16 + 4 = 20).
Counting electrons in a molecule is an essential part of understanding the chemical properties of a material. With the information from a periodic table of the elements, and some straightforward arithmetic, you can calculate the number of electrons based on the chemical formula of a material. This information can be used to design chemical reactions, predict properties, and much more.


Leave a Comment