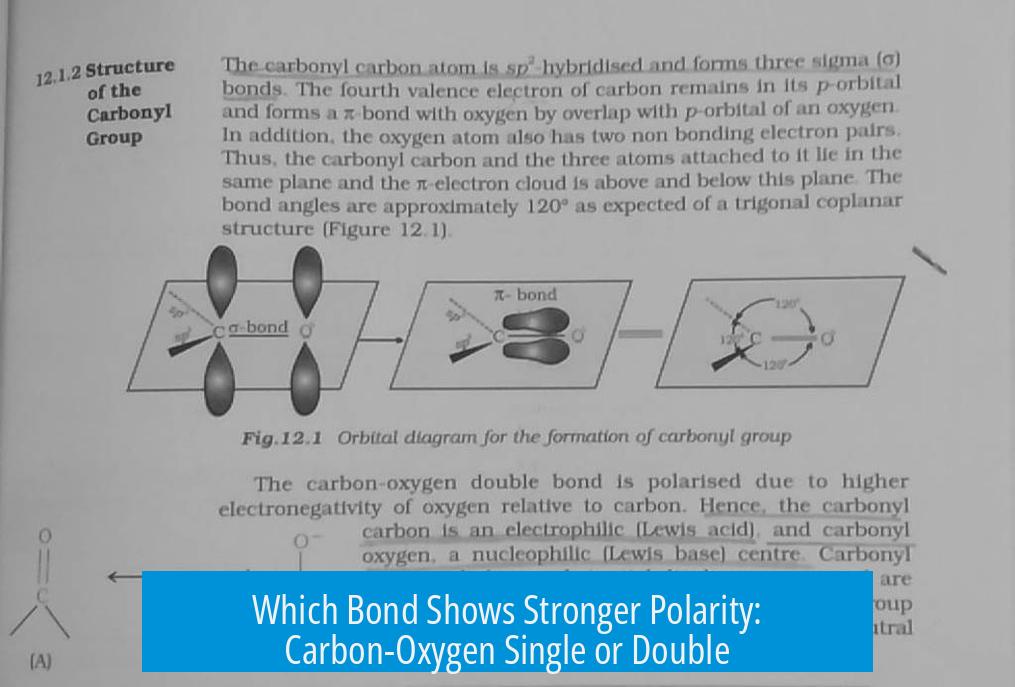
Which Has a Stronger Polarity: Carbon-Oxygen Single or Double Bond?
The carbon-oxygen double bond (C=O) has a stronger polarity than the carbon-oxygen single bond (C-O). This difference arises from not only the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen but also resonance contributions intrinsic to the double bond.
Polarity in Carbon-Oxygen Single Bond (C-O)
The C-O single bond is polar mainly because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. This creates a polar sigma (σ) bond where electron density shifts toward oxygen, giving it a partial negative charge.
- The bond polarity depends solely on the difference in electronegativity.
- There are no resonance or additional bonding effects increasing polarity.
Polarity in Carbon-Oxygen Double Bond (C=O)
The C=O double bond shows stronger polarity due to two factors:
- Electronegativity Difference: Similar to C-O, oxygen attracts electrons strongly.
- Resonance Effects: The pi (π) bond allows resonance structures where oxygen carries a partial negative charge more significantly.
Resonance stabilizes the bond and increases the partial charges on atoms, enhancing the bond’s polarity.
Reactivity as Evidence for Bond Polarity
The electrophilic nature of the carbon in the C=O bond is more pronounced. It reacts readily with nucleophiles, unlike the typical C-O single bond unless chemically activated. This reactivity highlights the stronger bond polarity in C=O.
Contextual Influences on Polarity
Polarity varies with bonding context:
- Surrounding groups attached to carbon or oxygen influence actual polarity and behavior.
- For example, alcohols with C-O bonds show strong hydrogen bonding, affecting solubility and physical properties despite lower intrinsic bond polarity.
- Ketones with C=O bonds are more polar intrinsically but exhibit different solubility due to lack of hydrogen bonding.
Key Takeaways
- C=O bonds are more polar than C-O bonds due to electronegativity and resonance.
- The single C-O bond polarity arises from sigma bond electronegativity difference only.
- C=O bonds act as electrophiles, showing stronger polarity through nucleophilic reactions.
- Bond polarity may vary depending on the molecular environment and substituents.




Leave a Comment