Difference Between KMnO4/NaOH and OsO4/NaHSO3 H2O in Syn Dihydroxylation
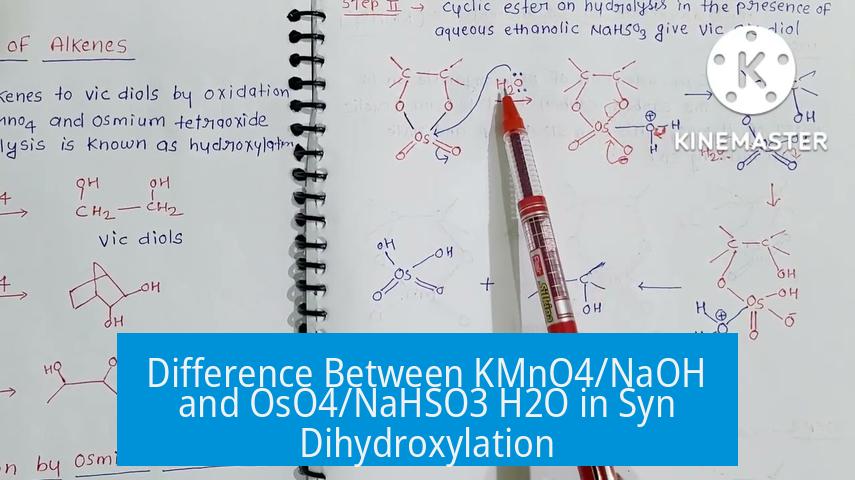
KMnO4/NaOH and OsO4/NaHSO3 H2O differ primarily in reactivity, selectivity, cost, and toxicity for syn dihydroxylation reactions. KMnO4 is a strong, less selective oxidizer, whereas OsO4 is a mild, selective reagent. The choice depends on substrate sensitivity and desired reaction control.
Reactivity and Selectivity
- OsO4: Selectively reacts with carbon–carbon double bonds to form vicinal diols. It does not oxidize other functional groups such as alcohols. This selectivity gives cleaner products when sensitive groups are present.
- KMnO4: Acts as a strong oxidizing agent. It can oxidize double bonds but also targets other oxidizable groups, often leading to over-oxidation and less control.
Functional Group Tolerance
OsO4 tolerates other functional groups like alcohols. The reaction proceeds without affecting these groups, preserving the integrity of complex molecules.
KMnO4 may oxidize multiple sites, which can be problematic in multifunctional substrates. This broad reactivity is less suitable when selectivity is critical.
Cost and Toxicity
| Aspect | KMnO4/NaOH | OsO4/NaHSO3 H2O |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Cheap and readily available | Expensive due to osmium content |
| Toxicity | Less toxic; safer handling | Highly toxic and requires careful handling |
When to Use Each Reagent

- KMnO4/NaOH: Suitable when broad oxidation is acceptable or the substrate can tolerate strong oxidizing conditions. Often selected for cost-sensitive processes or robust molecules.
- OsO4/NaHSO3 H2O: Preferred for selective syn dihydroxylation of double bonds in complex molecules with multiple functional groups. It is ideal when preserving non-target groups is essential despite higher cost and toxicity.
Summary
Choose OsO4 for controlled, selective syn dihydroxylation with minimal side reactions. KMnO4 offers a cost-effective alternative but risks over-oxidation and lower selectivity.
Key Takeaways
- OsO4 is mild, selective for alkenes, and preserves other functional groups.
- KMnO4 is a strong oxidizer, less selective, and may affect multiple sites.
- Cost and toxicity favor KMnO4; selectivity and mildness favor OsO4.
- Use OsO4 for sensitive molecules; use KMnO4 for robust or cost-sensitive applications.




Leave a Comment