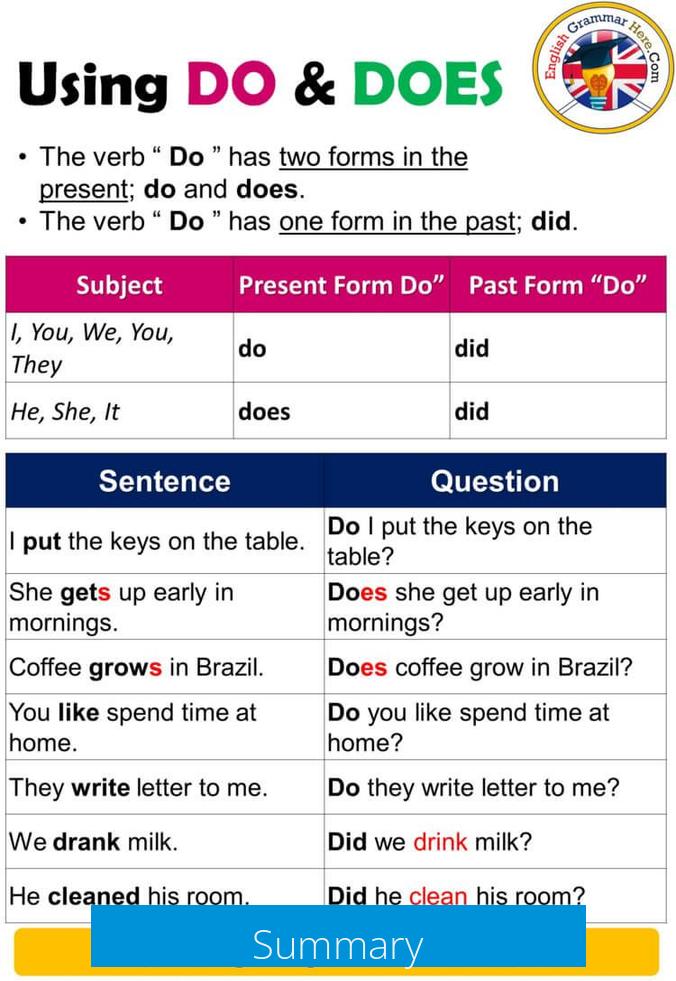
Does Eumelanin Affect the Shade of Red Hair?

Eumelanin does not directly affect the shade of red hair; rather, red hair color primarily depends on the amount of pheomelanin produced. However, because eumelanin and pheomelanin levels are inversely related, eumelanin can indirectly influence red hair shades by regulating the availability of pheomelanin.
Melanin Types and Their Roles
Hair color is determined by two main types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin.
- Eumelanin produces brown to black hair tones.
- Pheomelanin is responsible for red to yellowish hues, including shades of red hair.
People with red hair have higher levels of pheomelanin and very low levels of eumelanin.
Inverse Relationship of Melanin Production

Melanocytes produce melanin, but increased production of one melanin type reduces the other.
- Higher eumelanin production leads to less pheomelanin.
- Less eumelanin allows greater pheomelanin accumulation, enhancing red tones.
Therefore, eumelanin does not create red shades but limits the amount of red pigment possible.
Genetic Influence on Melanin Production
Genes control melanin synthesis pathways, particularly MC1R and ASIP.
- Mutations in these genes influence which melanin predominates.
- MC1R mutations often reduce eumelanin, increasing pheomelanin and producing red hair.
Due to genetic variation, individuals show diverse red hair shades like auburn, strawberry blonde, and fiery red, reflecting different pheomelanin levels.
Summary
- Red hair color depends mostly on pheomelanin concentration.
- Eumelanin creates brown/black shades and does not directly produce red hair tones.
- An inverse production mechanism means eumelanin indirectly affects red shades by limiting pheomelanin.
- Genetic mutations regulate eumelanin and pheomelanin balance, driving hair color diversity.
Does Eumelanin Affect the Shade of Red Hair? A Deep Dive Into Hair Pigmentation
In short: Eumelanin does not directly affect the shade of red hair. Instead, it’s primarily pheomelanin that paints the vibrant reds, auburns, and strawberry blondes. However, eumelanin does have an indirect role by balancing pigment production—kind of like the yin to pheomelanin’s yang.
Curious how this pigment tug-of-war works? Hang tight as we unravel the fascinating pigment palette behind red hair. Whether you’re a redhead wondering why your shade isn’t exactly “fiery” or just a curious soul, this breakdown will clear the pigment fog.
The Melanin Tug-of-War: Eumelanin vs Pheomelanin

Hair color depends on two key pigments: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is the pigment behind brown and black hair colors. Pheomelanin, on the other hand, throws red into the mix, creating those unmistakable red hues.
Imagine melanocytes, the pigment factories in your hair follicles, have a limited budget for pigment production. If they spend most of it producing eumelanin, that usually means less pheomelanin gets made. The reverse is also true. In simple terms: produce more of one, get less of the other.
So, if someone has high eumelanin levels, you’re likely to see darker shades of hair, and if eumelanin levels are low, pheomelanin can shine through, producing red tones.
Why Red Hair Is All About Pheomelanin
This pigment combo explains the core of the red hair mystery. The fiery reds, soft strawberry blondes, and deep auburns differ because of varying amounts of pheomelanin. The more pheomelanin, the more vibrant and rich the red shade.
To quote a pigment insider: “Pheomelanin is the star player in red hair color.” Eumelanin’s role there? Basically a supporting act, if even present at all.
So if you’re admiring a stunning redhead or thinking about dyeing your hair red, it’s good to know that the red pigments come primarily from variations in pheomelanin.
Genetics: The Puppet Master Behind the Pigment Show

Genes like MC1R and ASIP control the complex pathway of melanin production. Mutations in these genes dictate whether your melanocytes lean toward eumelanin or pheomelanin production.
Think of these genes as the pigment “switchboard operators” adjusting the volume of each melanin type. If MC1R changes, it can reduce eumelanin output and boost pheomelanin — a classic recipe for red hair.
This explains why red hair runs in families and why some people have that elusive perfect strawberry blonde shade, while others settle for auburn or fiery red.
Does Eumelanin Affect Red Hair Shade At All?
While eumelanin doesn’t directly color red hair, it indirectly affects its shade by limiting the total pheomelanin amount available. Since melanocytes can’t max out both pigments simultaneously, higher eumelanin means less pheomelanin and thus, a less vibrant red.
Imagine two gardeners sharing a patch of soil—if one plants more roses (eumelanin), fewer tulips (pheomelanin) get room to grow. So hair that’s “red” but mixed with eumelanin can appear as darker auburn or reddish-brown.
Real-World Tips: What This Means for You
- If you have red hair and want it brighter: Understand that your natural eumelanin levels may cap how fiery your hair looks. Hair dye can artificially boost pheomelanin-like pigments for a vibrant pop.
- Parents of redheaded kids: Genetic mutations in MC1R can inform expected hair color shades, but remember, pigment production is a balancing act. Siblings may differ even with similar genes due to pigment ratios.
- Curious about your hair’s shade? A DNA test focusing on MC1R and related genes can give some insight, but the best “test” remains seeing how your hair reacts to sunlight and the natural changes as you age.
The Bottom Line
Does eumelanin affect the shade of red hair? Yes, but only indirectly. It sets the stage by limiting the amount of pheomelanin, which is the key pigment behind the rich spectrum of red hair colors. Your hair’s shade dances between these two pigments, choreographed by genetics.
So next time you spot someone’s red mane—from strawberry blonde to deep auburn—remember: it’s mostly pheomelanin doing the heavy lifting, with eumelanin quietly in the background influencing the hue through a little pigment politics. Intriguing, isn’t it?
Got red hair questions or personal pigment stories? Share them below. Hair science never looked this fun!
Does eumelanin directly change the shade of red hair?
No, eumelanin does not directly affect red hair shade. Red hair color comes mainly from pheomelanin, which defines its different tones like strawberry blonde or auburn.
How does eumelanin indirectly influence red hair color?
Eumelanin production limits pheomelanin levels. Because they balance each other, higher eumelanin means less pheomelanin, which can affect how vibrant the red hair appears.
What genetic factors control eumelanin and pheomelanin levels?
Genes like MC1R and ASIP control melanin production. Mutations in these genes change the ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin, impacting hair color intensity and shade variation.
Can different amounts of eumelanin cause variations of red hair?
Variations in eumelanin mostly cause brown to black hair shades. However, its inverse relation with pheomelanin quantity can cause subtle differences in red hair brightness or depth.
Why do people with red hair have less eumelanin?
Red hair typically results from low eumelanin and high pheomelanin. The genetic pathways favor pheomelanin production, reducing eumelanin and giving red hair its characteristic color.




Leave a Comment