Why Are Oxidation Reactions Called Oxidation Reactions, and Reduction Reactions Called Reduction Reactions?
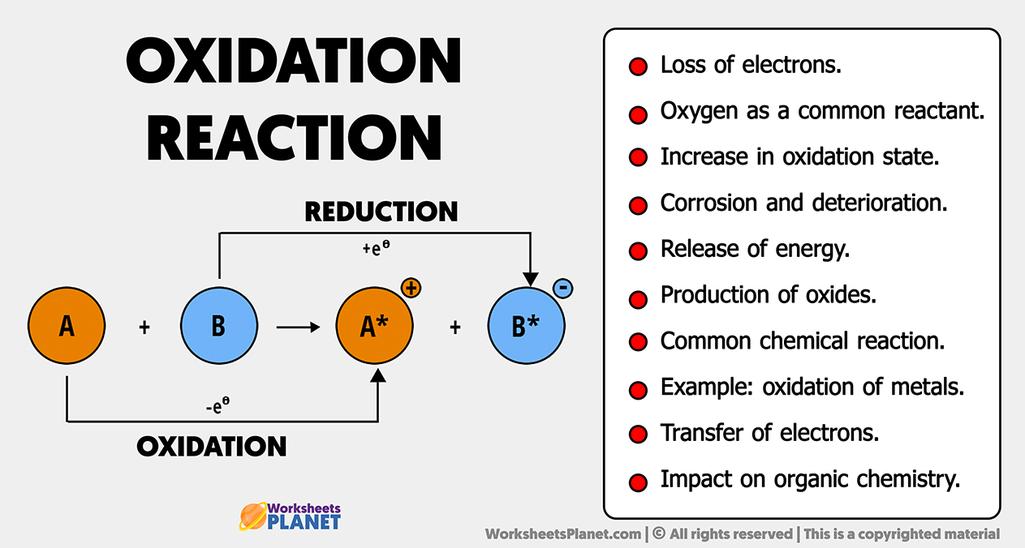
Oxidation reactions are named for the original observation that oxygen atoms caused substances to lose electrons, while reduction reactions describe the gain of electrons that lowers the charge on ions. These names stem from historical chemistry and metallurgy practices, which linked electron transfer to oxygen involvement and changes in ion charge.
Origin of the Term “Oxidation”
The term oxidation originates from early chemistry, where reactions with oxygen were first studied. Chemists noticed that many reactions involving oxygen caused substances to lose electrons.
- Initially, “oxidation” meant chemically reacting with oxygen.
- Later, scientists realized that substances could lose electrons without oxygen being present.
- Despite this, the term oxidation remained, now broadly applying to electron loss regardless of oxygen involvement.
This shift expanded oxidation to include reactions where other elements or agents remove electrons, not only oxygen. The name stuck because the initial understanding was tied closely to oxygen’s role.
Why is it Called Reduction?
The term reduction can seem counterintuitive since it involves gaining electrons. Electrons carry a negative charge, so gaining electrons lowers an atom’s or ion’s positive charge.
- “Reduction” refers to the reduction in overall charge, not the atomic or molecular mass.
- For example, a metal ion with charge +3 gains electrons, reducing its charge to +2 or 0.
Historically, reduction describes smelting metal ores.
- Metal ores are often oxides where metals exist in positive oxidation states.
- Heating ores with reducing agents like carbon removes oxygen and adds electrons.
- This process “reduces” the metal’s oxidation state to zero, yielding pure metal.
Summary of Origins and Definitions
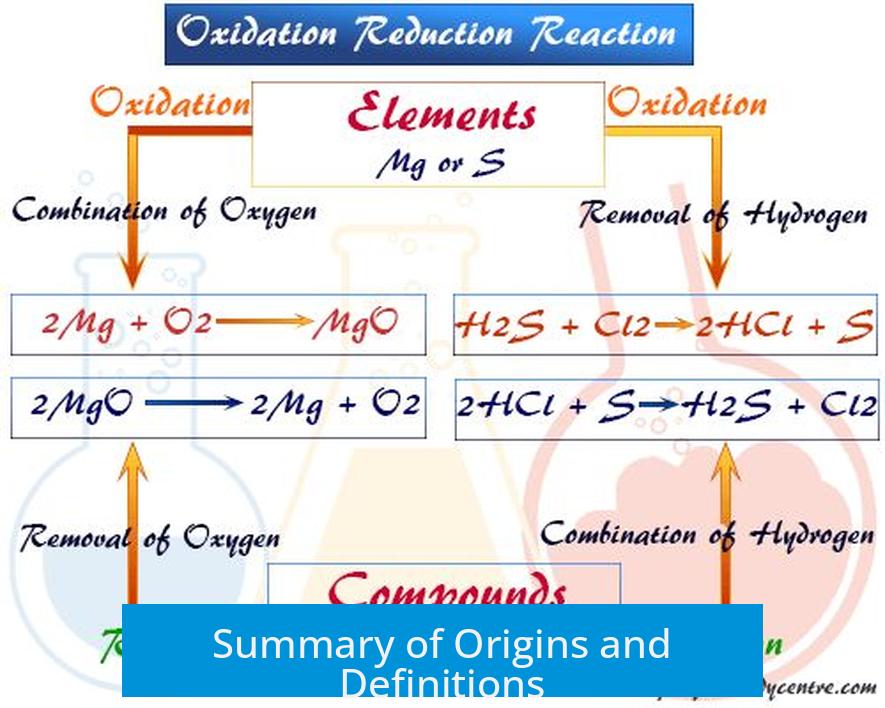
| Term | Initial Observation | Modern Meaning | Historical Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation | Reaction with oxygen | Loss of electrons | Oxygen involvement in early chemical reactions |
| Reduction | Smelting ores to metals | Gain of electrons, lowering ion charge | Removal of oxygen from metal ores, lowering oxidation state |
Key Takeaways
- Oxidation originally referred to reactions with oxygen causing electron loss.
- Now, oxidation means losing electrons, regardless of oxygen presence.
- Reduction means gaining electrons, which lowers positive charge on ions.
- The term reduction arose from metallurgical processes reducing metal ores to pure metals.
Why are oxidation reactions named after oxygen?
Oxidation reactions got their name from early chemists who saw oxygen causing changes in substances. They called it oxidation because oxygen was responsible for those reactions initially.
Do oxidation reactions always involve oxygen?
No. Originally, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. Later, scientists found similar reactions involved electron loss without oxygen. The term “oxidation” was kept because the behavior was the same.
Why is gaining electrons called reduction?
Reduction refers to lowering the charge of an ion. When an ion gains negatively charged electrons, its positive charge decreases. This “reduction” of charge gives the process its name.
What is the historical origin of the term reduction in chemistry?
Reduction comes from metallurgy. It described removing oxygen from metal ores to get pure metals. This involved adding electrons, which lowered the metal’s oxidation state.
How are oxidation and reduction connected?
Oxidation means losing electrons, while reduction means gaining electrons. They happen together in many reactions, balancing electron transfer between substances.




Leave a Comment