Understanding Enzyme-Based Cleaners
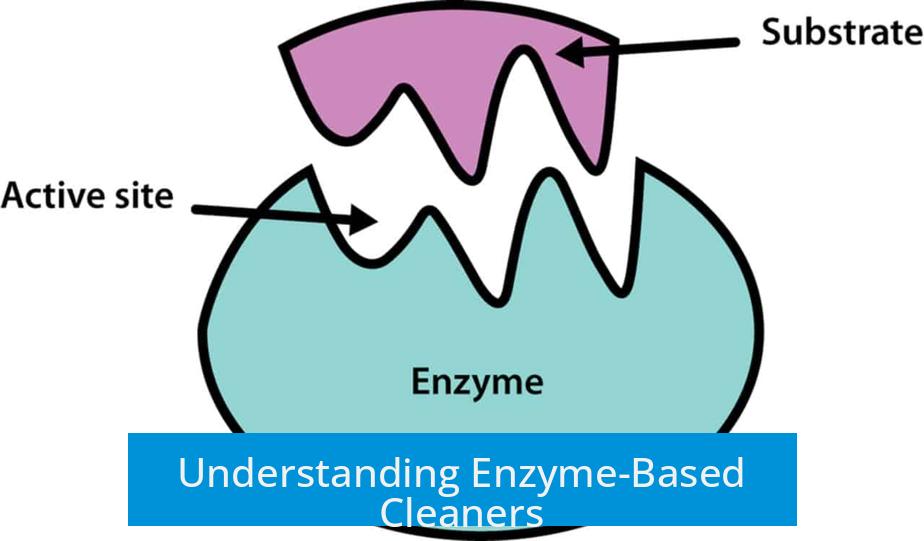
Enzyme-based cleaners use specific enzymes to break down different types of stains and soils, making them effective and environmentally friendly cleaning agents. These cleaners rely on biological catalysts rather than harsh chemicals. They are widely used in laundry detergents and various cleaning contexts.
Enzymes Used in Laundry Detergents
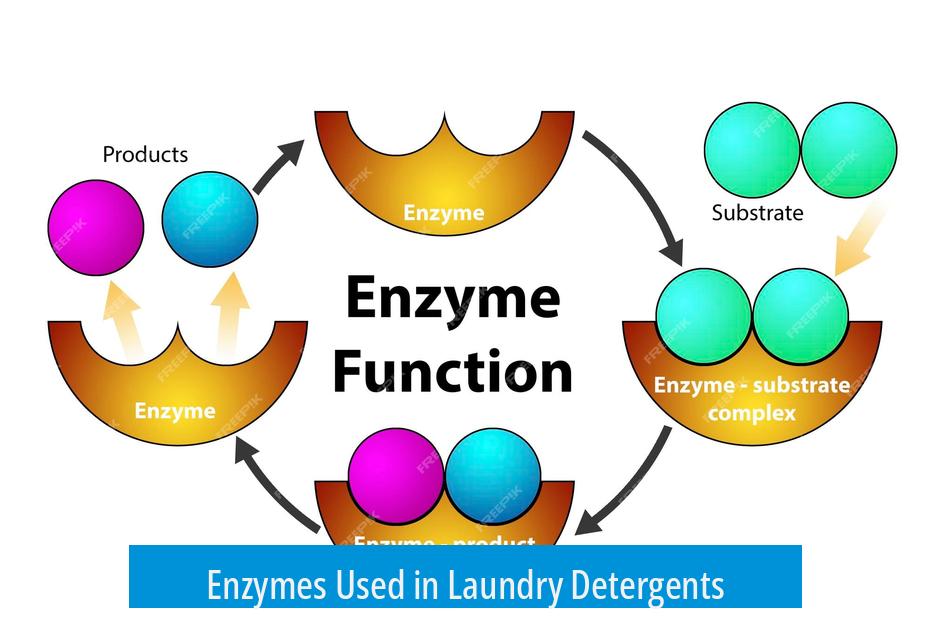
Enzymes make up about 30-40% of the global enzyme production, mostly for laundry detergents. They target specific stain types:
- Proteases: Break down proteins, effective against blood, egg, and gravy stains.
- Amylases: Degrade starch-based stains.
- Lipases: Target fats and grease, helping remove oily stains.
Many washing powders contain only one type of enzyme, but some formulations combine two or all three. For instance, BioZet promotes an entirely enzyme-based cleaner without bleaches or fluorescers, relying on mild surfactants for cleaning power.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Enzyme-based cleaners produce waste that is less harmful than traditional caustic cleaners. This allows easier and more cost-effective waste disposal, especially for industries. Instead of expensive chemical treatment, enzyme waste can often be sent to sewer systems directly.
For example, caustic waste disposal can cost about $1 per liter, with daily expenses reaching thousands of dollars in large operations. Using enzymes reduces these costs significantly by minimizing hazardous waste output.
Applications Beyond Laundry
Enzyme cleaners serve various roles outside laundry:
- Pool Cleaning: Enzyme pool cleaners help degrade organic matter, though specific enzymes used are not always disclosed.
- Stain Removal: Products with enzymes successfully remove difficult stains like animal urine. The exact enzyme types and their shelf stability remain areas of interest.
Key Takeaways
- Enzyme-based cleaners use proteases, amylases, and lipases to target proteins, starches, and fats.
- They reduce environmental impact by producing less harmful waste suitable for sewer disposal.
- Cost savings arise from lower waste treatment needs.
- Applications extend beyond laundry to pools and specialty stain removers.
- Formulations may combine multiple enzymes or rely solely on them with mild surfactants.
What types of enzymes are commonly found in laundry detergents and what do they target?
Proteases break down proteins like blood and egg stains. Amylases target starches, while lipases break down fats and grease. Some detergents contain one or a mix of these enzymes.
How do enzyme-based cleaners benefit industrial waste disposal?
These cleaners produce less harmful waste than traditional caustic cleaners. This allows discharge into sewer systems, avoiding expensive waste treatment costs, which can save facilities large sums daily.
Are enzyme-based cleaners stable over time, especially for stain removal?
The exact stability depends on the formulation. Some enzyme cleaners for stains, like those targeting animal urine, remain effective for months without losing activity, though specific enzymes used are often not disclosed.
Do enzyme-based laundry detergents include bleach or harsh chemicals?
Many enzyme-based detergents do not contain bleach or fluorescing agents. They rely on enzymes and mild surfactants to clean, making them gentler on fabrics and the environment.
Why does the global enzyme market favor laundry detergents?
About 30-40% of all enzymes produced globally go into laundry detergents. This is due to their ability to efficiently break down common stains, making detergent enzymes a major enzyme market segment.


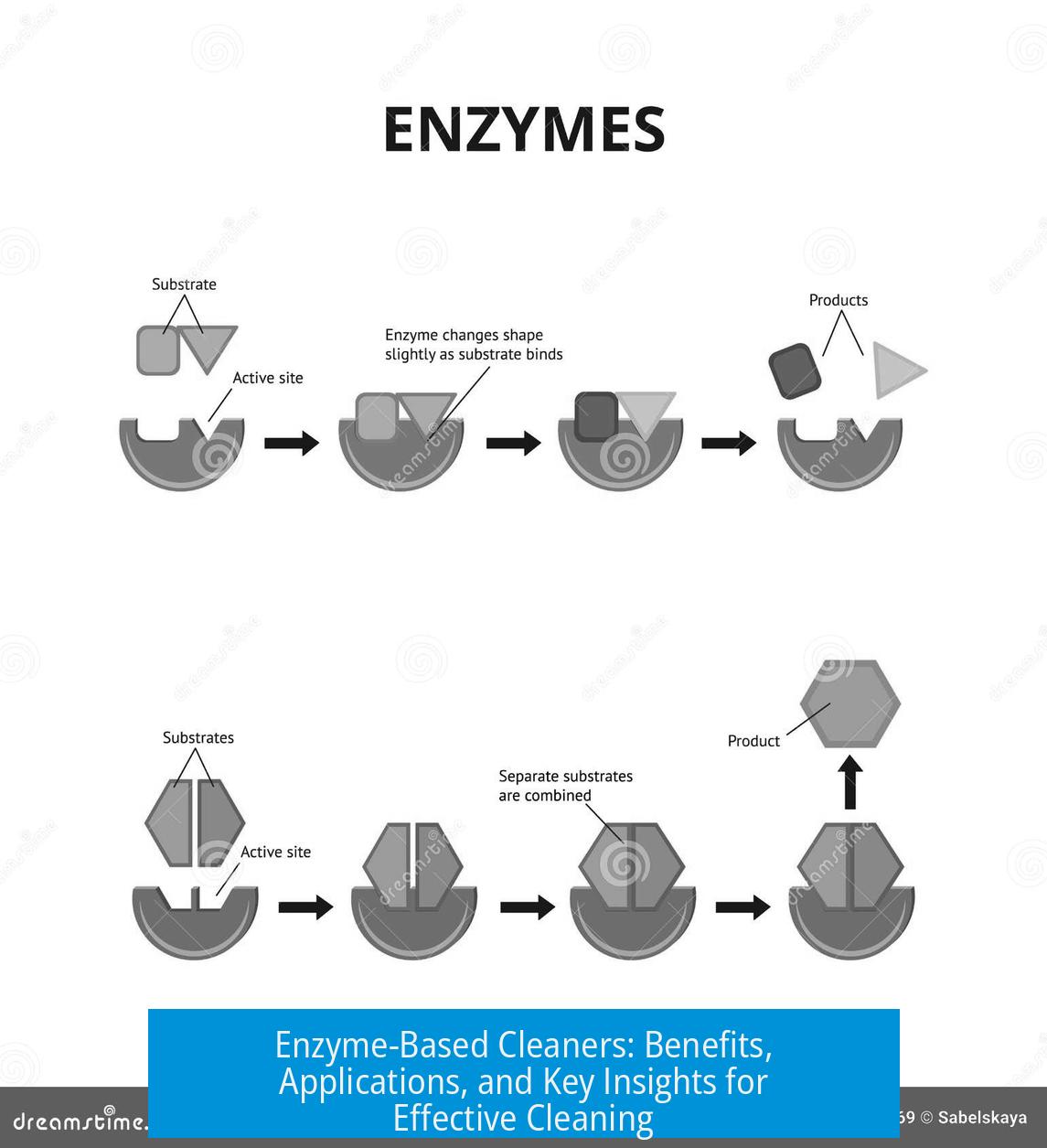

Leave a Comment