What is Squishiness in Liquids, Anyway?
Squishiness in liquids primarily refers to the sensation created by a combination of factors including viscosity and viscoelasticity, but it is not a property of the liquid alone. This texture usually arises from the interaction between the fluid inside an object and the object’s outer layer, especially in squishy toys.
Understanding Viscosity
Viscosity measures a liquid’s resistance to flow. It indicates thickness—honey has high viscosity, while water has low viscosity.
Viscosity impacts squishiness by controlling how the liquid inside resists movement. A thicker liquid moves slower under pressure, contributing to the “squish” feeling. However, viscosity alone does not create squishiness.
The Role of Viscoelasticity
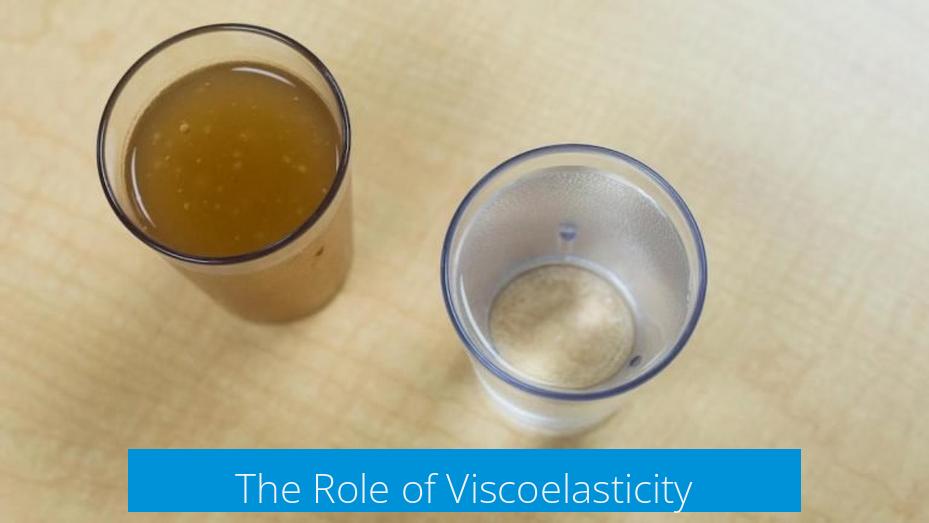
Viscoelastic materials show both fluid and solid behavior. Polymers in some gels behave like liquids when deformed slowly but act like solids under quick force.
In squishy toys, viscoelastic gels combine liquid-like flow with solid-like resistance. This dual nature helps the toy deform under pressure and slowly return to shape, enhancing the squishy sensation.
Composition of Squishy Toys
- Outer Layer: Usually made from elastic or plastic materials that resist deformation to some extent.
- Internal Filling: Typically a viscous liquid or gel, thick enough to provide resistance and slow movement inside.
The squishiness emerges from the interplay between the thick liquid inside and the flexible outer shell. The outer layer’s resistance combined with the liquid’s viscosity or gel’s viscoelastic behavior produces the tactile feedback experienced during squeezing.
Summary of Key Points
- Viscosity is the liquid’s thickness and resistance to flow.
- Viscoelastic materials combine fluid and solid traits, essential for squishy textures.
- Squishiness comes from both the liquid inside and the toy’s outer layer.
- The liquid’s properties alone do not determine squishiness; the container matters.
What does squishiness in liquids mainly depend on?
Squishiness largely depends on viscosity, or how thick a liquid is, and the resistance of the outer layer of the material. Together, these control how the liquid inside responds to pressure.
How does viscoelasticity relate to the squishiness of toys?
Viscoelastic materials act like solids and liquids at different times. Many squishy toys use gels, which show viscoelastic behavior by combining liquid-like flow with solid-like resistance.
Is the liquid inside a squishy toy solely responsible for its squishiness?
No, it’s not just the liquid. The outer layer’s resistance and thickness, along with the internal liquid, work together to create the squishy feel.
What materials are commonly used in making squishy office toys?
Simple plastic or elastic materials are often used. These materials form the outer layer and hold thick liquids or gels inside to achieve the squishy effect.
Why do gels in squishy toys behave differently than plain liquids?
Gels contain polymers that are loosely bound with liquid, giving them properties of both solids and liquids. This unique structure allows them to deform and then slowly return to shape.





Leave a Comment