Understanding Compounds, Molecules, Elements, and Atoms
Elements and Atoms
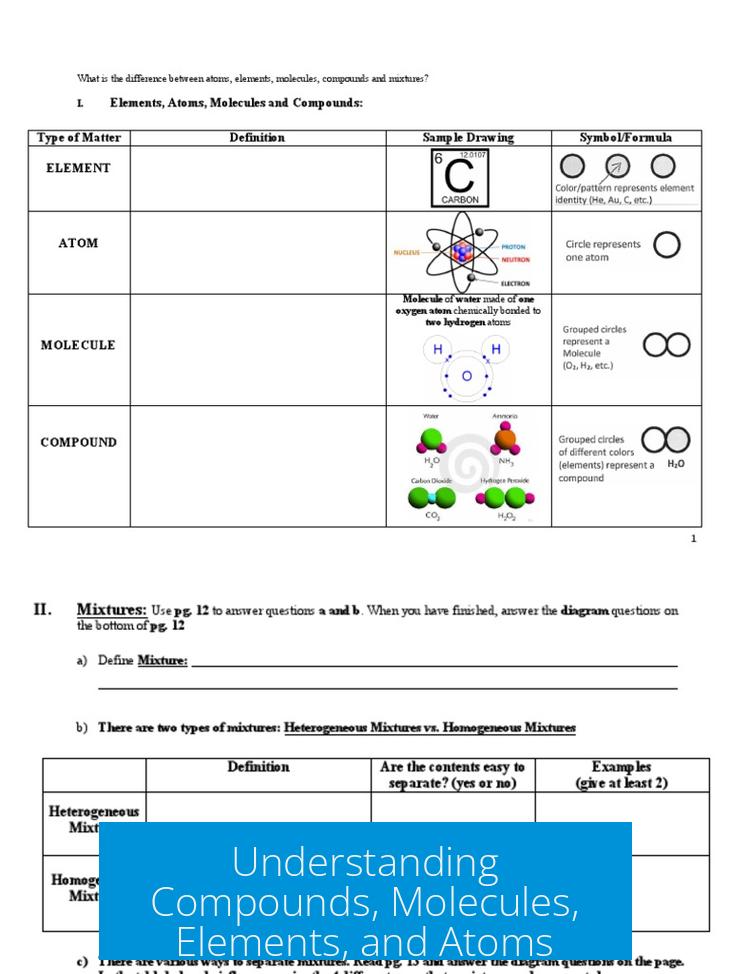
Elements represent specific kinds of atoms distinguished by their number of protons. Each element corresponds to atoms that share the same proton count, defining their identity uniquely. An atom is a physical structure composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The terms “element” and “atom” overlap often but differ fundamentally. An atom refers to a single particle, whereas an element refers to a category of atoms with shared properties due to proton number. For example, all hydrogen atoms, having one proton, define the hydrogen element.
Molecules
Molecules are groups of two or more atoms chemically bonded, primarily through covalent or ionic bonds. They are electrically neutral overall, meaning they carry no net charge. Molecules can consist of atoms from the same element or different elements.
- Example: O3 (ozone), composed of three oxygen atoms.
- Example: H2, a molecule of two bonded hydrogen atoms.
In nature, atoms are mostly found bonded as molecules rather than isolated.
Compounds
Compounds are a subset of molecules composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded. They are distinct because they involve multiple elements combined at the atomic level.
All compounds qualify as molecules, but not all molecules qualify as compounds because molecules may consist solely of one element.
- Example: NaCl (table salt), a compound of sodium and chlorine.
- Example: CO2 (carbon dioxide), a compound of carbon and oxygen.
Mixtures
Mixtures differ from compounds and molecules because they consist of two or more substances physically combined but not chemically bonded. Mixtures retain individual properties of their components.
Examples include salad mixtures or chocolate mixed with milk, where components coexist without fixed ratios or bonding.
Key Takeaways
- Atoms form the basic units of matter; elements are defined by atomic proton count.
- Molecules are bonded atoms, either from one element or multiple elements.
- Compounds are molecules containing at least two different elements.
- Mixtures combine substances physically, without chemical bonding.





Leave a Comment