Limonene: The Aromatic Terpene Found in Citrus Peels
Limonene is a terpene responsible for the citrus scent commonly detected in fruit peels, especially lemons and oranges, and is present as the (R)-enantiomer known as D-limonene in many citrus fruits. It ranks among the top five terpenes by concentration in cannabis, contributing to fragrance profiles in strains like Super Lemon Haze and Chernobyl.
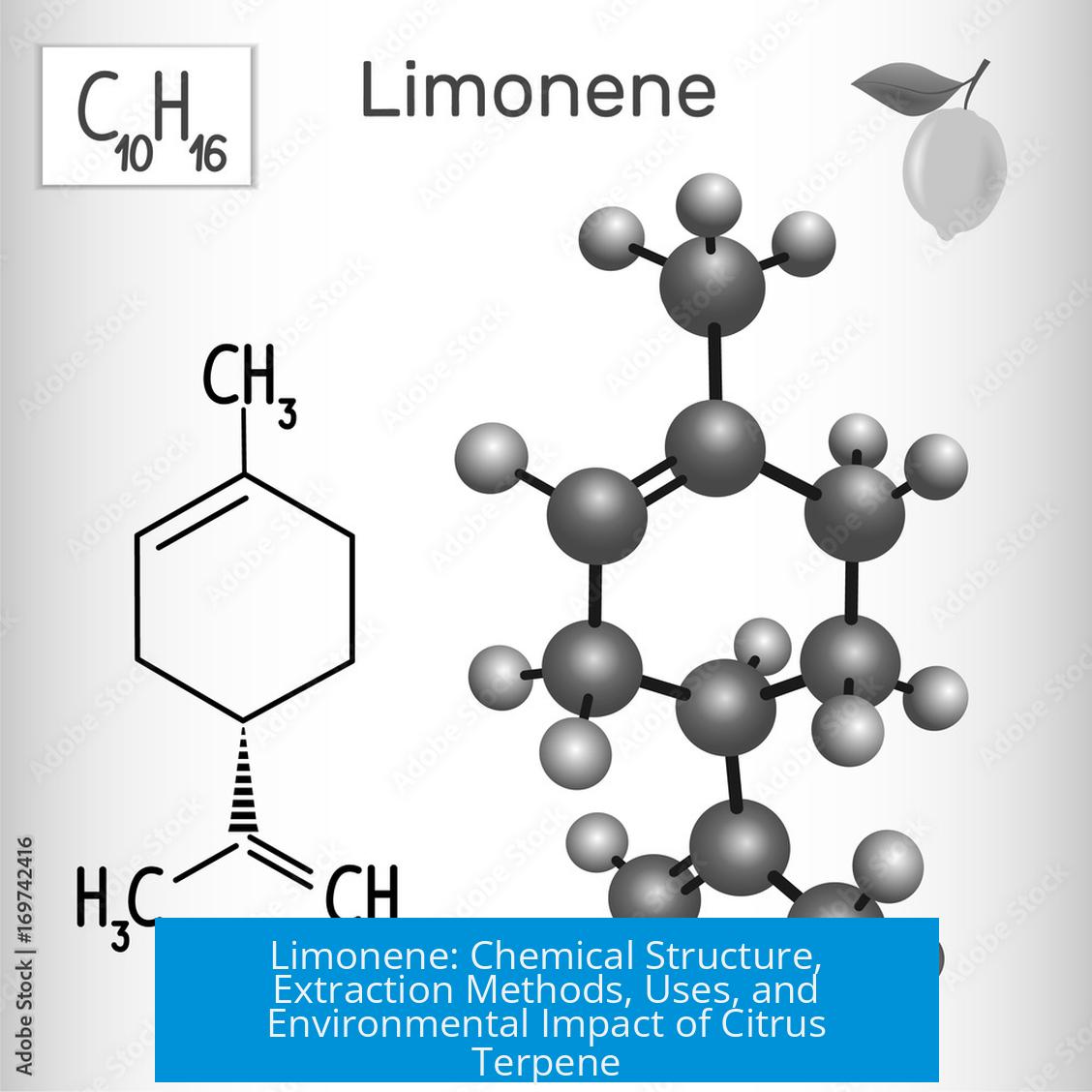
Chemical Structure and Isomers
Limonene is a chiral hydrocarbon with two enantiomers: (R)-limonene (D-limonene) and (S)-limonene (L-limonene). The (R)-enantiomer predominates in citrus peels, imparting their characteristic scent. Despite being called “aromatic” in terms of smell, limonene does not possess aromatic rings chemically.
Extraction Methods
Commercial limonene is mainly extracted through steam distillation or centrifugal separation. These methods isolate the essential oil containing D-limonene from citrus peels efficiently, allowing for large-scale production used across industries.
Applications and Uses
- In Cannabis: Limonene enriches aroma and taste profiles, making it popular in various cannabis strains.
- Industrial: D-limonene serves as a less toxic solvent than xylene in histology for clearing dehydrated tissue samples.
- Solvent Properties: It effectively dissolves support materials like high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) in 3D printing and acts as a solvent for essential oils and alkaloids.
- Other Uses: Limonene is investigated as an additive in rocket fuel and utilized as a grease solvent, offering environmental and safety advantages compared to alternatives.
Biological and Environmental Impact
Limonene functions as a botanical insecticide due to its strong citrus scent, which also deters cats. However, it poses risks such as skin irritation (contact dermatitis) on direct application and toxicity to aquatic organisms. As a flammable liquid, careful handling is necessary.
Some studies highlight limonene’s potential health benefits, including reducing glucose and cholesterol levels, which may contribute to metabolic regulation.
Additional Notes
- The term aromatic here refers exclusively to the scent, not chemical aromaticity.
- User experiences vary regarding limonene’s flavor when found in cannabis, with some disliking its dominance.
- Limonene’s unique scent has inspired artistic creations such as tattoos.
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Chemical Form | Chiral terpene hydrocarbon, mainly D-limonene in citrus |
| Extraction | Steam distillation, centrifugal separation |
| Main Uses | Fragrance, solvent, insecticide, cannabis terpene profile |
| Biological Effects | Skin irritant potential; insect-repelling; modest metabolic benefits |
Key Takeaways
- Limonene is the key terpene behind the citrus peel aroma and found majorly as D-limonene in nature.
- It is commercially extracted via steam distillation or centrifugal means from citrus peels.
- Used in cannabis, industrial solvents, insecticides, and 3D printing industries.
- Presents both benefits and risks biologically and environmentally.
- The term “aromatic” relates to scent, not chemical structure.
What is the difference between the R- and S-enantiomers of limonene?
Limonene has two enantiomers: R- and S-. The R-enantiomer, called D-limonene, is found in citrus fruits. The S-enantiomer occurs in some coniferous trees. Their scents vary slightly, with R-limonene giving the familiar citrus smell.
How is limonene extracted commercially from citrus peels?
Commercial limonene is mainly obtained by steam distillation or centrifugal separation of citrus peels. These methods efficiently separate the terpene without degrading its structure or scent.
What are some industrial uses of limonene outside of aromatics?
D-limonene serves as a solvent to dissolve materials like high-impact polystyrene. It replaces toxic solvents like xylene in histology. It can also be used as a rocket fuel and a solvent for cryogenic grease.
Does limonene have any effects on humans or pets?
It can cause skin irritation upon contact. Cats dislike its strong scent, making it useful to deter them from plants. It is flammable in liquid form and toxic to aquatic life, so handle it carefully.
Is limonene an aromatic molecule in chemical terms?
No, limonene is not aromatic chemically. The term “aromatic” here refers to its citrus smell, not to having an aromatic ring in its molecular structure.



Leave a Comment