Potassium Nitrate Mixed with Stannous Fluoride
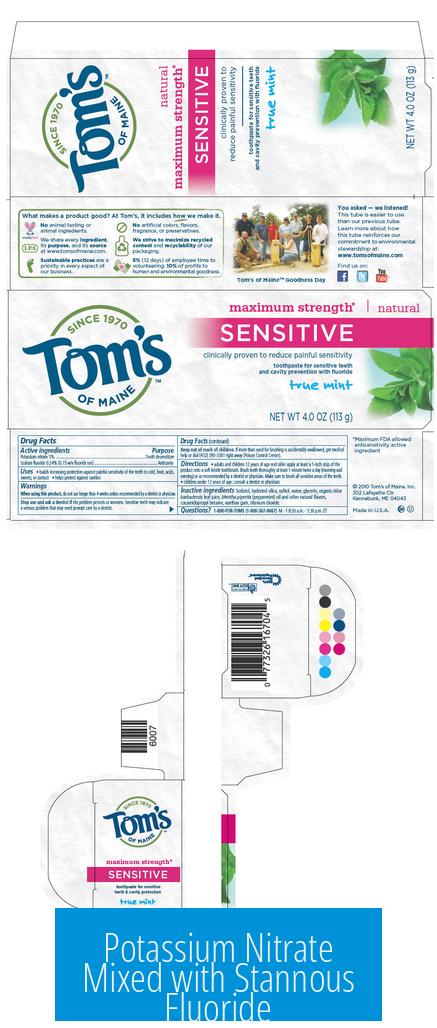
Potassium nitrate mixed with stannous fluoride can coexist in toothpaste but generally does not chemically react. The mixture requires careful formulation to maintain stability and effectiveness, as stannous fluoride is prone to oxidation in the presence of nitrate ions.
Presence in Toothpaste Formulations
Recent toothpaste formulations, such as the new Colgate Total (late 2024), include both potassium nitrate and stannous fluoride. This marks a development where both ingredients provide combined benefits: potassium nitrate acts as a desensitizing agent, while stannous fluoride offers antibacterial and anticavity effects.
Chemical Compatibility and Reactions
- Stannous chloride (similar to stannous fluoride in oxidation behavior) does not react directly with potassium nitrate. Mixing them causes stannous compounds to oxidize, forming less active tin dioxide, which lowers effectiveness.
- Potassium nitrate can react with water present in the formulation to form potassium hydroxide, increasing alkalinity. This shift can potentially harm tooth enamel if not carefully controlled.
Because of these effects, manufacturers often avoid directly mixing stannous chloride with potassium nitrate solutions to maintain the active stannous ion levels.
Stability in Toothpaste Formulation
Stannous fluoride’s stability poses challenges. The stannous ion (Sn(II)) easily oxidizes to less active Sn(IV) forms, especially in the presence of nitrate ions (NO3−). This oxidation reduces the ingredient’s efficacy for antibacterial and anti-caries action.
Potassium nitrate is commonly combined with sodium fluoride in products because sodium fluoride is more chemically stable and does not risk oxidation issues with nitrate ions. The combined use with stannous fluoride demands advanced stabilization techniques.
Practical and Market Considerations
- Some companies may prefer to market potassium nitrate and stannous fluoride separately to maintain ingredient stability and efficacy.
- This strategy also diversifies product lines, allowing consumers to select products tailored to specific dental needs, such as sensitivity management or antibacterial action.
Chemical Identity and Application Notes
Potassium nitrate is a white crystalline salt used in fertilizers and explosives. Stannous fluoride, also crystalline, is notable for its dental applications, particularly in reducing tooth decay and sensitivity. Their combination in toothpaste leverages complementary action but requires careful formulation to avoid loss of activity.
Key Takeaways
- Potassium nitrate and stannous fluoride coexist in some toothpastes but tend not to chemically react.
- Stannous fluoride oxidation by nitrate ions reduces its antibacterial efficacy.
- Potassium nitrate can increase formulation alkalinity through potassium hydroxide formation.
- Manufacturers use stabilization strategies or separate products to maintain ingredient effectiveness.
- Market trends reflect combining or separating ingredients based on efficacy and consumer choice.


Leave a Comment