Difference Between NaBH4 and LiAlH4 in Alcohol Reactions

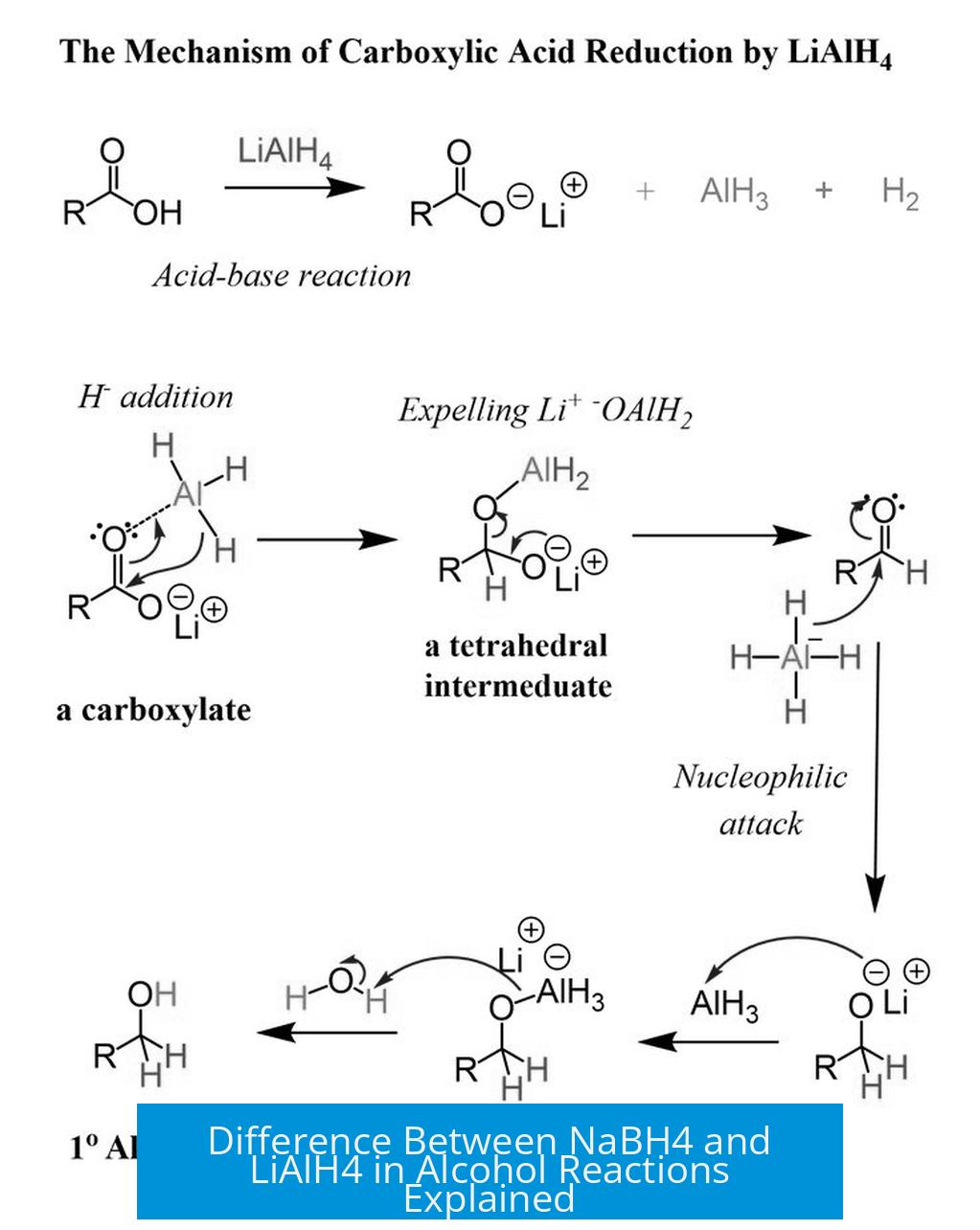
The main difference is that LiAlH4 is a much stronger reducing agent than NaBH4, capable of reducing a broader range of carbonyl compounds, including carboxylic acids and esters, but it is incompatible with alcohol solvents, whereas NaBH4 is milder, selectively reducing primarily aldehydes and ketones, and can be used in alcoholic solvents.
1. Reducing Strength and Scope
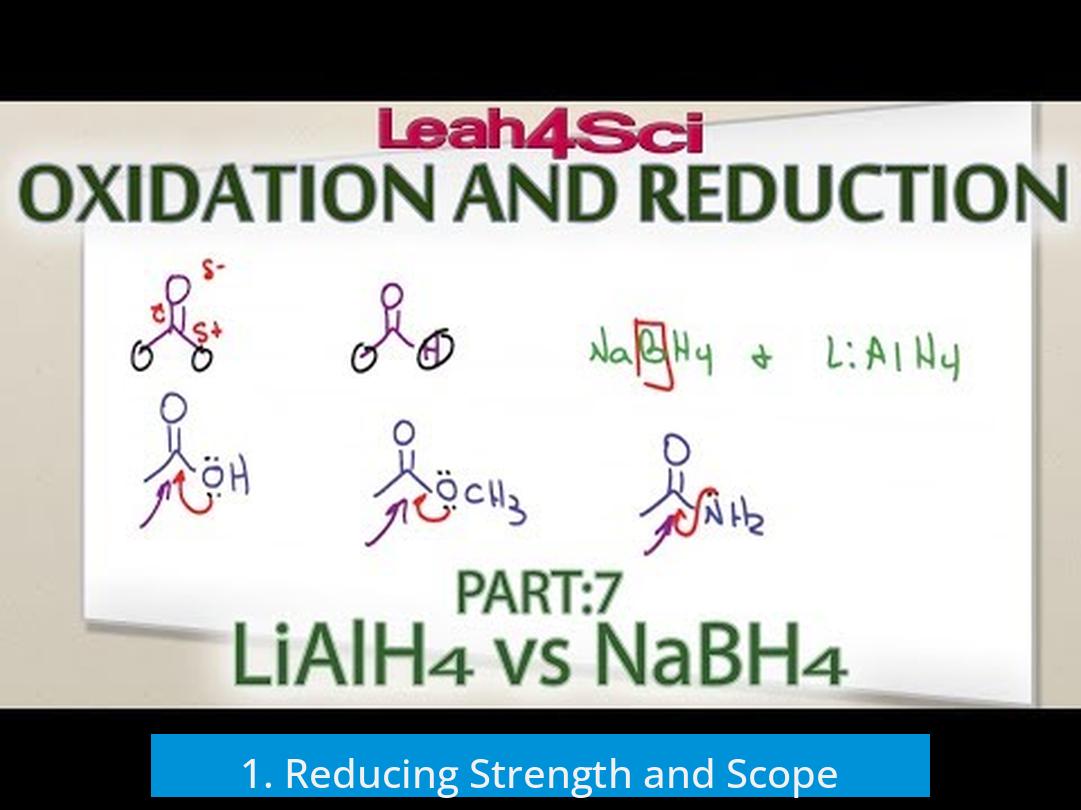
- LiAlH4 reduces almost all carbonyl groups: aldehydes, ketones, esters, and carboxylic acids.
- NaBH4 typically reduces only aldehydes and ketones and is much less reactive with esters and acids.
- LiAlH4’s broader scope makes it essential for compounds resistant to NaBH4.
2. Chemical Reasons Behind Reactivity Differences
- The key lies in their primary reducing elements: aluminum in LiAlH4 and boron in NaBH4.
- Aluminum’s lower electronegativity results in weaker Al-H bonds compared to B-H bonds, increasing LiAlH4’s reactivity.
- The lithium ion (Li+) stabilizes intermediate states better than sodium (Na+), enhancing LiAlH4’s effectiveness.
3. Solvent Compatibility
- LiAlH4 reacts violently with alcohols, making it unsuitable for reductions in alcoholic solvents.
- NaBH4 is stable in protic solvents like methanol and ethanol, allowing it to be used directly in alcohol media.
4. Practical Selection in Alcohol Reactions
- When only aldehydes or ketones require reduction, especially in alcohol solvents, NaBH4 is preferred due to safety and ease.
- LiAlH4 is chosen for challenging reductions outside the scope of NaBH4, but with solvents like ethers, not alcohols.
Summary of Key Differences
| Aspect | NaBH4 | LiAlH4 |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Strength | Mild; aldehydes and ketones | Strong; includes esters and acids |
| Solvent Compatibility | Compatible with alcohols | Incompatible with alcohols |
| Primary Reducing Element | Boron (B-H bond) | Aluminum (Al-H bond) |
Both reagents have defined roles in synthetic chemistry based on their reactivity and solvent requirements. Selecting between them depends on substrate type, solvent choice, and reduction strength needed.



Leave a Comment