Is mRNA from the Parent Cell Shared Between Daughter Cells?
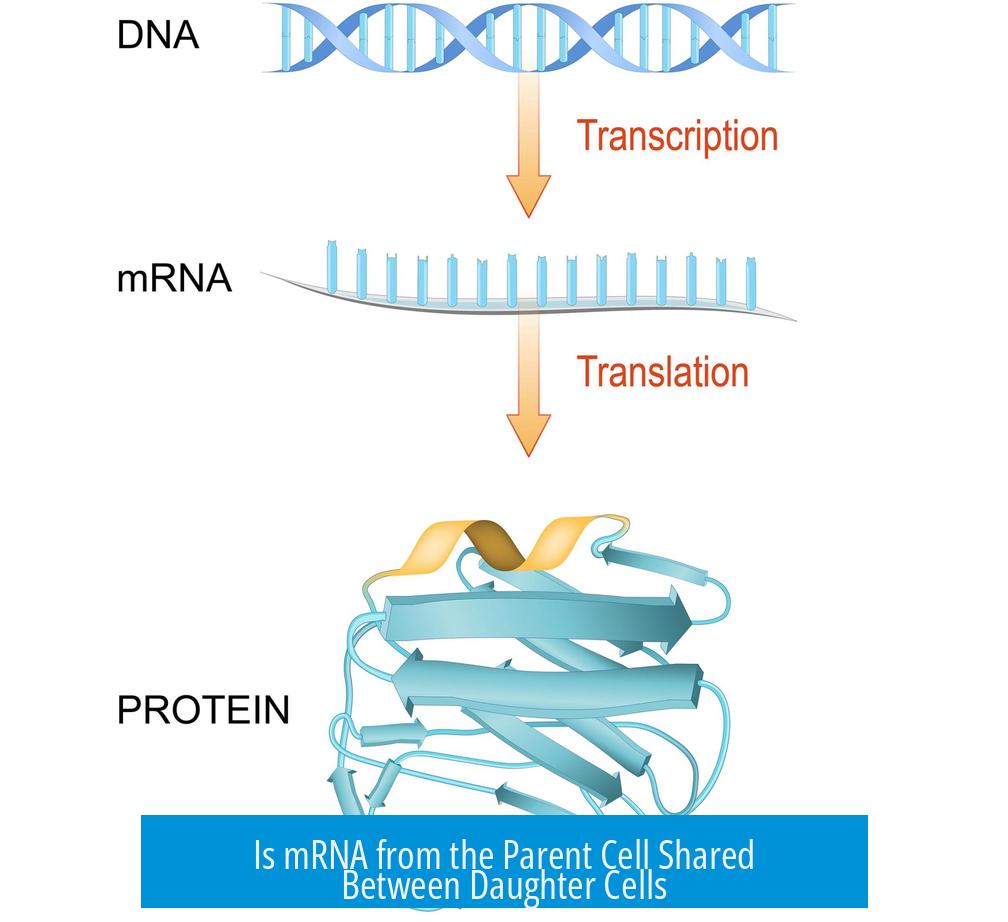
mRNA from the parent cell can be distributed between daughter cells during cell division but does not persist long. The daughter cells mainly rely on synthesizing new mRNA from their own DNA after division.
mRNA Distribution During Cell Division
In cell division, some free-floating mRNA present in the cytoplasm of the parent cell can be split between the two daughter cells. This process is passive and depends on the cellular contents being divided.
However, mRNA molecules are inherently unstable. They degrade rapidly once outside their original transcription site.
- Transferred mRNA does not last long after division.
- Daughter cells cannot depend on inherited mRNA for ongoing protein synthesis.
DNA Replication and New mRNA Transcription
The essential genetic material, DNA, is duplicated before cell division. Each daughter cell receives a full copy of the DNA.
This genetic blueprint enables each daughter cell to independently produce new mRNA molecules through transcription.
- DNA provides the code for mRNA synthesis.
- Daughter cells activate their own transcription processes post-division.
- New mRNA production ensures continuous protein synthesis and cell function.
Contrast With mRNA Vaccines
mRNA introduced by vaccines enters cells but does not integrate into cellular DNA. Thus, it is not inherited during cell division.
Vaccine mRNA serves a temporary role, initiating immune responses before being degraded.
- Vaccine mRNA is transient and non-heritable.
- It does not affect the genetic material passed to daughter cells.
Key Takeaways
- Parent cell mRNA can be shared briefly but degrades quickly in daughter cells.
- Daughter cells rely mainly on their own DNA to transcribe new mRNA.
- DNA replication ensures genetic continuity, enabling fresh mRNA production.
- mRNA vaccines do not alter DNA and are not passed to daughter cells.
1. Is mRNA from the parent cell shared directly with daughter cells during division?
Yes, some mRNA present in the parent cell’s cytoplasm can be split between daughter cells during division. However, this mRNA is unstable and degrades quickly after cell division.
2. Do daughter cells rely on inherited mRNA or new mRNA transcription?
Daughter cells primarily transcribe new mRNA from their own DNA. The mRNA inherited from the parent cell does not last long and is degraded soon after division.
3. How is DNA related to mRNA production in daughter cells?
During division, DNA is duplicated and evenly divided between daughter cells. Each daughter cell uses this DNA as the template to produce its own mRNA for protein synthesis.
4. Does mRNA from vaccines get passed to daughter cells?
No. mRNA introduced by vaccines does not integrate into cellular DNA and is not inherited by daughter cells. It is temporary and degrades after triggering an immune response.
5. Why doesn’t parent cell mRNA persist in daughter cells?
mRNA molecules degrade rapidly due to their chemical nature. Daughter cells need fresh mRNA transcribed from their own DNA to maintain normal function after division.



Leave a Comment