Opposite of “Dense”: Is There a General Term Chemically or Physically?
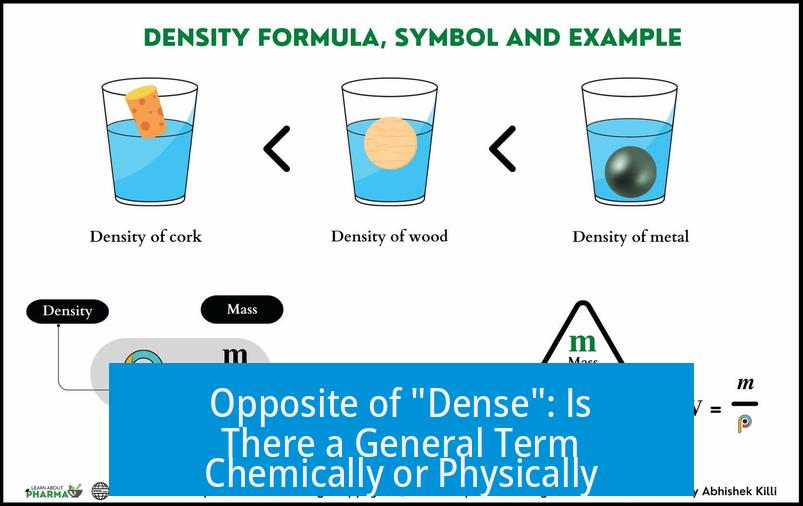
There is no single, universally accepted term that serves as the direct opposite of “dense” across all chemical and physical contexts. Instead, several words describe the concept of lower density or reduced compactness depending on the specific field or situation. Density itself is a quantitative property with a continuous scale, making exact opposites uncommon.
Understanding Density and Its Nature
Density measures mass per unit volume in physical materials. In chemistry, it can also refer to the compactness of molecules, atoms, or charge distributions. Because density is a scalar value, it ranges from low to high values rather than having true binary opposites. Scientists prefer numerical comparisons (e.g., low density vs. high density) over specific antonyms.
Density often describes material compactness, particle packing, or the concentration of charge or mass. Its opposite varies with the property discussed, such as structural morphology, gas pressure, or molecular distribution.
Common Opposites of Dense by Context
| Context | Suggested Opposite Terms | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Material Density | Low density, Light, Sparse, Rarefied, Loose, Fluffy | Indicates less mass per volume or less compactness; “light” contrasts with heavy. |
| Porosity or Morphology | Porous, Aerated, Voided | Describes materials with holes, cavities, or gas inclusions reducing density. |
| Charge Distribution in Chemistry | Diffuse, Disperse | Refers to spread-out charge or particles rather than concentrated presence. |
| Polymer or Network Crosslinking | Sparsely, Loosely, Lightly Crosslinked | Describes fewer connections, leading to less dense networks. |
| Gas or Fluid Phase | Rarefied, Vacuum, Void | Represents gases of very low pressure or near-empty spaces. |
Theoretical Perspective
Density does not have an intrinsic opposite like temperature has hot and cold. Instead, it represents a gradient from low to high density. This means “opposite” terms often describe qualitative differences, such as the presence of voids or reduced particle number per volume. Some argue “rare” or “rarefied” come closest to a general antonym by indicating less compactness or fewer entities in a space.
Terms like “sparse” describe discrete object distributions and suggest spacing rather than compactness. Sometimes, “diffuse” describes spread-out charge or matter distributions, but it is domain-specific and less used as a mass density antonym.
Practical Use in Science
- Scientists commonly quantify density numerically and compare values explicitly instead of using adjectives alone.
- Descriptive terms like “light,” “porous,” or “aerated” help describe materials qualitatively but depend on context.
- In phase diagrams, one may encounter “dense phase” versus “dilute phase,” which imply higher and lower densities without strict antonyms.
- In polymer science, describing networks as “densely crosslinked” versus “loosely crosslinked” gives relative density context within that structure.
Summary of Key Points
- “Dense” lacks a single universal opposite word chemically or physically.
- Opposites vary by context: “sparse,” “rarefied,” “light,” “porous,” and “diffuse” are common but specialized.
- Density is a graded property, better described by quantitative comparisons than strict antonyms.
- Terms like “vacuum” or “void” represent extreme low-density conditions, particularly in gases or space.
- Scientists prefer numeric density data and contextual descriptors over relying on absolute opposites.




Leave a Comment