Welcome to the fascinating world of electrons! If you are interested in learning about the electron configurations of elements, you have come to the right place.
Electron configurations are an important tool for understanding the properties of elements. In this article, we will explore what electron configurations are, how they are used, and which element has the following electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3.
Atoms are composed of tiny subatomic particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons. Electrons are the smallest and most mobile particles in the atom and their distribution in the atom’s orbitals determines the properties of the element. This distribution of electrons is called the electron configuration.
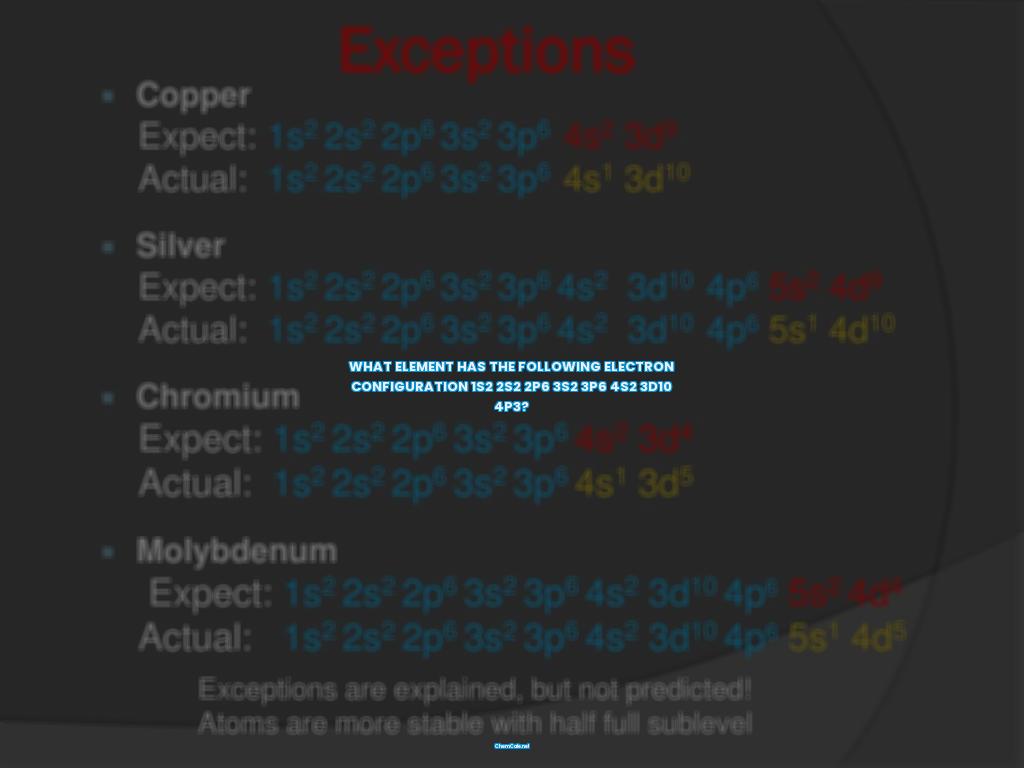
The electron configuration of an element is written using the standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1.
Electron configurations are used for a variety of reasons. They are used to determine the valency of an element (which describes how many bonds it can form with other elements), to predict the properties of a group of elements, and to interpret atomic spectra.
Now, let’s take a closer look at our main question: which element has the following electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3?
The answer is sulfur! Sulfur has an atomic number of 16 and has the following electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. This electron configuration is often abbreviated as [Ne] 3s2 3p4.
We hope this article has helped you understand what electron configurations are and how they are used. If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We are always happy to help.
What element has the following electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3?
Electron configurations are an important concept in understanding the properties of elements. By looking at the electron configuration of an element, we can understand the number of electrons present in each of its atomic orbitals and determine the element’s valence. The electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3 is the electron configuration for the element Selenium.
What are Electron Configurations?
Electron configurations refer to the arrangement of electrons in the shells and subshells of an atom. This arrangement is determined by the energy levels of the electrons, and can be written using a standard notation. Each energy level is represented by a principal quantum number (n), and each subshell is represented by an azimuthal quantum number (l). For example, the electron configuration of sodium is written as 1s22s22p63s1.
The electron configuration of an element is important in understanding its physical and chemical properties. Elements with similar electron configurations tend to exhibit similar properties, and the electron configuration of an element can be used to predict its valence. Additionally, electron configurations are used to interpret atomic spectra.
Notation
The electron configuration of an element is written using a standard notation. This notation consists of a sequence of subshells, each labelled with the shell number (given by the principal quantum number), the subshell name (given by the azimuthal quantum number) and the total number of electrons in the subshell in superscript. For example, if two electrons are filled in the ‘s’ subshell of the first shell, the resulting notation is ‘1s2’.
History of Electron Configurations
The notation for the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of atoms came into practice shortly after the Bohr model of the atom was presented by Ernest Rutherford and Niels Bohr in the year 1913. However, it was only in the 1920s that the modern electron configuration notation was developed.
Conclusion
The electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3 is the electron configuration for the element Selenium. Electron configurations are an important concept in understanding the properties of elements, as they can be used to determine the element’s valence and predict its properties. The electron configuration of an element is written using a standard notation which consists of a sequence of subshells, each labelled with the shell number, the subshell name and the total number of electrons in the subshell in superscript. The notation for the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of atoms came into practice shortly after the Bohr model of the atom was presented in 1913.
Which element has the following electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 quizlet?
Electron configurations are essential for understanding the properties of an element. They can be used to determine the valency of an element, predict the properties of a group of elements, and interpret atomic spectra. This notation for the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of atoms was developed shortly after the Bohr model of the atom was presented by Ernest Rutherford and Niels Bohr in 1913.
What is an Electron Configuration?
An electron configuration is a notation for the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of atoms. It is written using subshell labels, which include the shell number (given by the principal quantum number), the subshell name (given by the azimuthal quantum number), and the total number of electrons in the subshell (in superscript).
For example, if two electrons are filled in the ‘s’ subshell of the first shell, the resulting notation is ‘1s2’. The electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation, with all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1.
What is the Electron Configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10?
The electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 can be used to represent the element zinc (Zn). The electron configuration of zinc shows that it has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, six electrons in the 2p orbital, two electrons in the 3s orbital, six electrons in the 3p orbital, two electrons in the 4s orbital, and ten electrons in the 3d orbital.
What are the Uses of Electron Configurations?
Electron configurations are useful for several applications in chemistry. They can be used to determine the valency of an element, predict the properties of a group of elements (elements with similar electron configurations tend to exhibit similar properties), and interpret atomic spectra. The electron configuration of an element also provides information on its chemical reactivity, magnetic properties, and other physical properties.
In addition, electron configurations can be used to understand the structure of molecules and the behavior of electrons in chemical reactions. By examining the electron configuration of an atom, chemists can predict how the atom will interact with other atoms and molecules in a chemical reaction.
In conclusion, electron configurations are an essential tool for understanding the properties of an element. The notation 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 can be used to represent the element zinc (Zn). Electron configurations are useful for determining the valency of an element, predicting the properties of a group of elements, and interpreting atomic spectra. They can also be used to understand the structure of molecules and the behavior of electrons in chemical reactions.
Which element has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3?
Electron configurations are important in chemistry as they help us to determine the valency of an element, predict the properties of a group of elements, and interpret atomic spectra. The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals.
Notation
The notation for the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of atoms came into practice shortly after the Bohr model of the atom was presented by Ernest Rutherford and Niels Bohr in the year 1913. Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1.
The electron configuration of an atom is written with the help of subshell labels. These labels contain the shell number (given by the principal quantum number), the subshell name (given by the azimuthal quantum number) and the total number of electrons in the subshell in superscript. For example, if two electrons are filled in the ‘s’ subshell of the first shell, the resulting notation is ‘1s2’.
Which Element Has An Electron Configuration Of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3?
The element with an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3 is Scandium (Sc). Scandium is a chemical element with the atomic number 21 and is a member of the group 3 elements in the periodic table. Its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 4p3.
Scandium is a silvery-white metallic element that is relatively rare in nature. It is a hard and brittle metal that is most commonly found combined with other elements in minerals. Scandium is used in a wide range of applications, including alloys, lasers, and lighting.
Uses of Electron Configurations
The electron configurations of elements are very useful in chemistry. They can be used to:
- Determine the valency of an element.
- Predict the properties of a group of elements (elements with similar electron configurations tend to exhibit similar properties).
- Interpret atomic spectra.
Knowing the electron configuration of an element can help chemists understand how it will interact with other elements, allowing them to make better predictions about the outcome of reactions. It also helps us to better understand the structure and behavior of atoms.
In conclusion, the element which has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3 is Scandium (Sc). Electron configurations are an important part of chemistry, as they can help us to determine the valency of an element, predict the properties of a group of elements, and interpret atomic spectra.
Which element has the following electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1?
The answer to this question is the element Carbon, with an atomic number of 6. Electron configurations are used to represent the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. The electron configuration of an atom describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals.
What are Electron Configurations?
Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1. Table of Content However, the standard notation often yields lengthy electron configurations (especially for elements having a relatively large atomic number).
Why are Electron Configurations Useful?
Electron Configurations are useful for:
- Determining the valency of an element.
- Predicting the properties of a group of elements (elements with similar electron configurations tend to exhibit similar properties).
- Interpreting atomic spectra.
This notation for the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of atoms came into practice shortly after the Bohr model of the atom was presented by Ernest Rutherford and Niels Bohr in the year 1913. In this notation, the energy level is n while the subshell is l. The number of electrons in the subshell is represented by e.
How do Electron Configurations Relate to Valency?
The electron configuration of an atom is elucidated using the Aufbau principle which states that the lowest energy subshell is first filled up with electrons, followed by the next higher energy subshell, and so on. This principle helps in understanding the valency of an element. Valency is the number of electrons that an atom can lose, gain, or share in order to form a chemical bond with another atom.
For example, consider the element Carbon (C) with an atomic number of 6. The electron configuration of Carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2. Here, the valency of Carbon is 4, as it can form four chemical bonds (by sharing or donating four electrons) with other atoms.
In conclusion, the element having the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 is Carbon, with an atomic number of 6. Electron configurations are used to represent the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. Electron Configurations are useful for determining the valency of an element, predicting the properties of a group of elements, and interpreting atomic spectra. The Aufbau principle helps in understanding the valency of an element.
Which of the following elements has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1?
It is essential to understand electron configurations in order to gain a better understanding of how atoms are constructed and how electrons are distributed in their orbitals. The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence.
What are Electron Configurations?
The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1.
However, the standard notation often yields lengthy electron configurations (especially for elements having a relatively large atomic number). This can make it difficult to quickly find the electron configuration of an element, and so it is important to understand a few shortcuts.
Understanding Electron Configurations
In order to understand which element has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1, it is important to understand the notation used to represent electron configurations. The notation consists of the following elements:
- s: This represents the s-orbital, which can hold up to two electrons.
- p: This represents the p-orbital, which can hold up to six electrons.
- d: This represents the d-orbital, which can hold up to ten electrons.
- f: This represents the f-orbital, which can hold up to fourteen electrons.
The electron configuration of an element is a shorthand representation of how many electrons are in each orbital, and the order of the orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1, which means that it has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, six electrons in the 2p orbital, two electrons in the 3s orbital, and one electron in the 3p orbital.
The Correct Answer
Now that we understand the notation used to represent electron configurations, we can answer the question: which of the following elements has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1?
The electron configuration of Si (atomic number 14) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2. Thus, this option is incorrect. The electron configuration of Mg (atomic number 12) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2. Thus, this option is the correct choice. The correct answer is option E.
An atom of element Na (atomic number 11) contains 11 electrons. The electron configuration of this element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1. Hence, this option can be neglected. The electron configuration of Ne (atomic number 10) is 1s2 2s2 2p6. Thus, this option is incorrect. The atomic number of Al is 13, and it contains 13 electrons which are arranged as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1. Thus, this option is incorrect.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question of which of the following elements has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 is Mg (atomic number 12). Understanding electron configurations is essential for understanding the structure of atoms.
Which of the following elements has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3?
Electron configurations are an important part of understanding the behavior of atoms and their interactions with other atoms. In order to determine which element has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3, it is important to understand the basics of electron configurations and the Aufbau Principle.
What are Electron Configurations?
Electron configurations are a way of describing the arrangement of electrons in an atom. This arrangement is based on the principle that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. Electron configurations are typically written in terms of the element’s atomic number and the subshells of the atom’s orbital shells.
For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s22s22p63s1. This means that the sodium atom has two electrons in its innermost orbital (1s2), two in its second orbital (2s2), six in its third orbital (2p6), and one in its fourth orbital (3s1).
Filling of Atomic Orbitals and the Aufbau Principle
The Aufbau Principle states that electrons will occupy orbitals of lower energy before occupying higher energy orbitals. This principle is based on the fact that the energy of an orbital is calculated by the sum of the principal and the azimuthal quantum numbers.
Therefore, using the Aufbau Principle, the electron configuration of magnesium (atomic number 12) can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2. This means that the magnesium atom has two electrons in its innermost orbital (1s2), two in its second orbital (2s2), six in its third orbital (2p6), and two in its fourth orbital (3s2).
Which Element Has the Electron Configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3?
Using the Aufbau Principle, the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 is chlorine (atomic number 17). This means that the chlorine atom has two electrons in its innermost orbital (1s2), two in its second orbital (2s2), six in its third orbital (2p6), two in its fourth orbital (3s2), and three in its fifth orbital (3p3).
In conclusion, the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 is chlorine (atomic number 17). To determine this, it is important to understand the basics of electron configurations and the Aufbau Principle. Electron configurations are a useful tool for understanding the behavior of atoms and their interactions with other atoms.



Leave a Comment