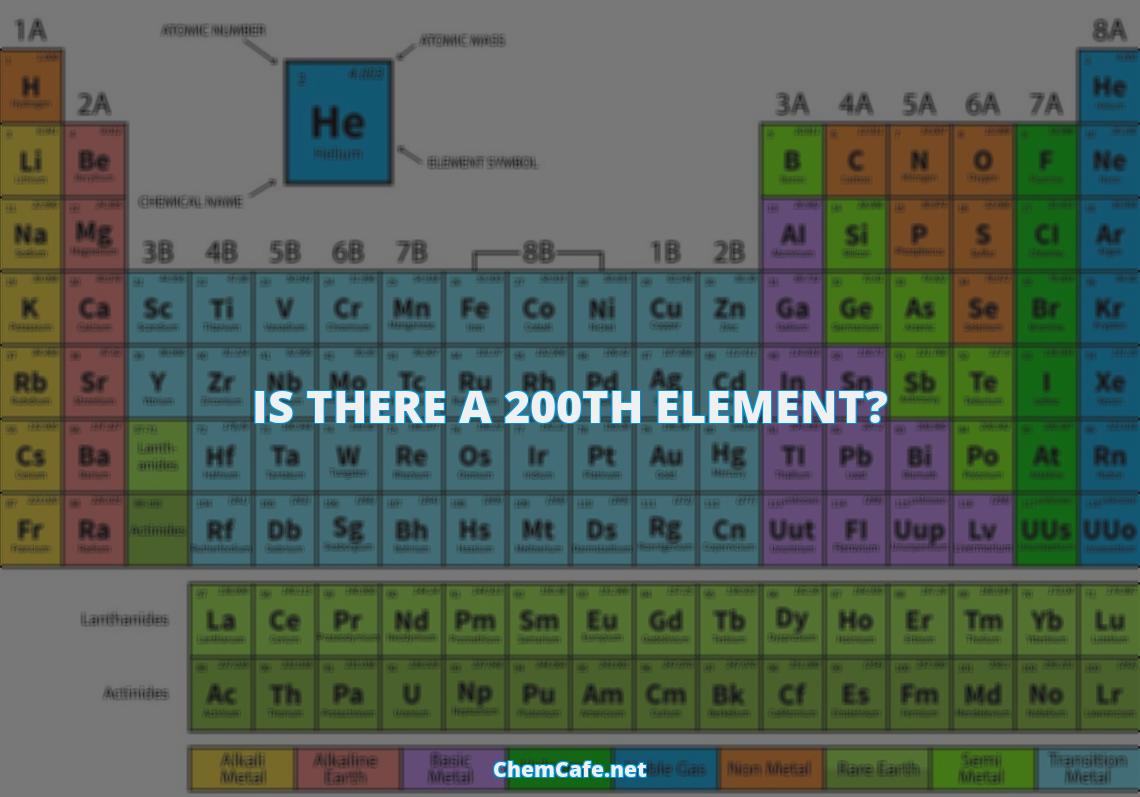
Elementary, my dear readers! Are you ready to explore the fascinating world of the periodic table and discover the 200th element? Have you ever wondered what the 200th element might be? Or what the 84th element is? Or even what the 72nd element is? Well, you’re in luck. We’re about to take a tour through the periodic table and discover some of its secrets.
As you know, the periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, which are organized by their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is a powerful tool used by chemists and physicists to understand the properties of the elements and their compounds. But what about element 200? Is there a 200th element?
The answer is yes, there is a 200th element. Polonium-200 atom is a polonium atom with an atomic number of 200, and it is a radioisotope of polonium. It has a half-life of about 140 days and is used in nuclear reactors for neutron flux control. But what about element 140? Is it possible? According to some theories, Corbomite (Ct) is a chemical element with an atomic number of 140, but it has yet to be identified.
But what about the rarest element ever? Astatine is a chemical element with symbol At and atomic number 85. It is the rarest naturally occurring element in the Earth’s crust, occurring only as the decay product of various heavier elements. And what about element 119? Ununennium, also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the hypothetical chemical element with symbol Uue and atomic number 119.
So, let’s dive into the periodic table and explore the secrets of the 200th element. Let’s explore the properties of the rarest element ever, the mysterious element 140, and the alluring element 119. Are you ready? Then let’s get started!
Is there a 200th element?
The periodic table of elements is a chart that contains all the known elements in the universe. It is divided into rows and columns, and each element is assigned a unique atomic number. But is there a 200th element?
The answer is yes, there is a 200th element. Polonium-200 atom is a polonium atom with an atomic number of 200. It is a radioactive element that is found in uranium-bearing ores and is typically found in minute amounts in nature. Polonium-200 is used in various industrial and medical applications and is also used as a source of neutrons in nuclear reactors.
What is the 150th element?
The 150th element is Schrodium, which is the provisional non-systematic name of a theoretical element with the symbol So and atomic number 150. Schrodium was named in honor of Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961), who developed his equation for quantum mechanics.
Is element 140 possible?
Yes, element 140 is possible. According to this, Corbomite (Ct) is a chemical element with atomic number 140. However, in real-life science, element 140 has yet to be identified.
Based on both the Seaborg and Pyykkö extended periodic tables described above, element 119 will be the start of period 8 and it will be an alkali metal.
What’s the rarest element ever?
Astatine is the rarest element ever. It is a chemical element with the symbol At and atomic number 85. It is the rarest naturally occurring element in the Earth’s crust, occurring only as the decay product of various heavier elements.
Ununennium and unbinilium (elements 119 and 120) are the elements with the lowest atomic numbers that have not yet been synthesized: all the preceding elements have been synthesized, culminating in oganesson (element 118), the heaviest known element, which completes the seventh row of the periodic table.
Is there a 119th element?
Yes, there is a 119th element. Ununennium, also known as eka-francium or element 119, is the hypothetical chemical element with symbol Uue and atomic number 119. It is expected to have properties similar to those of the other alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium, and is expected to be a silver-white metal.
Ununennium, if it were ever to be synthesized, would be the first element to be created with the use of a particle accelerator. It is also expected to be very unstable and to decay quickly into other elements.
The discovery of element 119, if it were ever to be made, would open up a whole new area of research in the field of the periodic table of elements. It would also provide us with a better understanding of the structure of matter, and could potentially lead to the discovery of new elements beyond what is currently known.
In conclusion, element 200 is Polonium-200 atom, element 150 is Schrodium, element 140 is Corbomite, Astatine is the rarest element ever, Ununennium and unbinilium are the elements with the lowest atomic numbers that have not yet been synthesized, and element 119 is Ununennium.
What is the 200th element?
Element 200 is Polonium-200 (symbol Po-200). This element is a radioactive metal discovered in 1898 by Marie and Pierre Curie. It is considered to be the first element to be discovered through the process of radioactivity. Polonium-200 has the atomic number 84 and is classified as a member of the family of elements known as chalcogens.
Polonium-200 Atom: Properties and Uses
Polonium-200 is a very unstable element. Its half-life is only 138.4 days, meaning it decays into other elements over time. It is also highly toxic, with a fatal dose only being a few micrograms. As such, it is used in very low concentrations and for very specific purposes.
One of the main uses for Polonium-200 is in nuclear power plants and other industrial applications. It is used as a source of neutrons for irradiating materials, and for controlling nuclear fission reactions. It is also used in nuclear medicine for diagnosing and treating certain types of cancer.
Polonium-200 has also been used in some specialized applications in the electronics industry. It is used as a source of charged particles for implanting into semiconductor devices, and it is also used in the manufacture of certain types of transistors.
What is the 150th Element?
The 150th element is Schrodium (symbol So). This element was first proposed in 2004 by the German chemist Erwin Schrodinger, who proposed a new form of the periodic table which included an element with atomic number 150.
Schrodium is an extremely rare element, with no known natural sources. It is believed to be the result of the decay of heavier elements, and is thought to have a half-life of around 10 minutes.
Despite its rarity, Schrodium has a wide range of potential uses. In particular, it has been suggested that it could be used as a catalyst in chemical reactions, and it is also thought to have potential applications in the medical field.
Is Element 140 Possible?
Element 140, known as Corbomite (symbol Ct), is a theoretical element that has yet to be discovered. It is believed to be a member of the group of elements known as “superheavy elements”.
These elements are extremely rare, and are thought to only exist in small amounts in the universe. They are thought to be the result of the decay of heavier elements, and also the fusion of lighter elements.
Element 140 is thought to have a half-life of around 10 days, and is believed to have potential applications in the medical field. It is also thought to have potential applications in the electronics industry.
What is the Heaviest Element Possible?
The heaviest element in terms of heaviest per a given number of atoms is the element with the highest atomic weight. This is the element with the largest number of protons, which is presently element 118, oganesson or ununoctium.
Oganesson is an extremely rare element, and is only found in trace amounts in nature. It is thought to have a half-life of around 0.89 seconds, and is believed to have potential applications in the medical and nuclear fields.
Is the Periodic Table Infinite?
The answer to this question depends on the definition of “infinite”. While there is no definitive answer, it seems likely that the periodic table is not infinite.
It is widely accepted that the periodic table represents all the known elements in the universe. As such, it is possible that new elements may still be discovered, but the number of elements is likely to remain finite.
It is also possible that the periodic table could be extended to include synthetic elements, or even theoretical elements. However, it is unlikely that these elements would ever become common enough to be included in the periodic table.
What is the 84th element?
The 84th element on the periodic table is Polonium, which is a relatively rare element. It is a member of the chalcogen family, which includes oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. Polonium is represented by the symbol Po, and has an atomic number of 84 and an atomic mass of 208.9824.
What are the Properties of Polonium?
Polonium has several oxidation states, the most stable being Po(IV) in aqueous solution. This gives rise to its most important chemical property: its tendency to hydrolyse and form colloids of Po(OH)4, in analogy with most tetravalent elements. It also forms soluble salts with chlorides, acetates, nitrates and other inorganic anions, but precipitates with sulfides.
Where is Polonium Found?
Polonium is found in the pitchblende, which is a mineral ore that is composed of uranium oxides. The pitchblende studied by the Curies contained only about 100 micrograms (millionths of a gram) of polonium per metric ton of ore. The element can now be prepared artificially in a particle accelerator, or “atom smasher.”
What are the Uses of Polonium?
Polonium is used in the production of static eliminators, which are devices that are used to remove static electricity from machines. It is also used in nuclear power plants as a neutron absorber, and in the production of certain types of semiconductors. It is also used in scientific research, and has been used in the past to create a radioactive source for treating certain types of cancer.
What is the History of Polonium?
Polonium was first discovered in 1898 by Marie and Pierre Curie, who were studying the pitchblende ore. They were able to identify the element by its tendency to hydrolyse and form colloids of Po(OH)4, which was a unique property of the element. They named the element after their native country of Poland.
Polonium is a relatively rare element, but its uses have grown over the years. It is used in the production of static eliminators, nuclear power plants, and certain types of semiconductors. It is also used in scientific research, and has been used in the past to create a radioactive source for treating certain types of cancer. The element was first discovered in 1898 by Marie and Pierre Curie, and was named after their native country of Poland.
What is the 72nd element?
The 72nd element is called hafnium, and it has a rather interesting history and some important commercial applications. It is a transition metal, and is number 72 on the periodic table. Its name comes from the Latin word for Copenhagen, where it was first isolated in 1922.
A Complicated Discovery
The discovery of hafnium was rather complicated. Element 72 falls at the boundary between transition metals and rare earth elements, so it was not clear which type it would belong to. Some chemists thought it would be a rare earth element and searched for it among minerals containing rare earths, but without success.
The breakthrough came in 1923, when the Dutch physicist Dirk Coster and the Hungarian-Swedish chemist George Charles von Hevesy discovered hafnium in Norwegian and Greenland zircons. They analyzed the X-ray spectra of the samples and were able to identify the new element, naming it hafnium after Copenhagen.
Properties
Hafnium is a ductile metal with a brilliant silvery lustre. It has a very low level of absorption of neutrons, which makes it useful in the nuclear power industry. It is also used in the making of super-alloys, which are materials that are resistant to extreme temperatures and pressures.
Uses
Hafnium has a variety of commercial applications. It is used in the production of thermionic converters, which are used to convert electrical energy into heat energy. It is also used in the production of alloys for the aerospace and automotive industries. In addition, hafnium is used in the production of semiconductors, which are used in computers and other electronic devices.
Hafnium is a fascinating element with a long and interesting history. It has a number of important commercial applications, such as its use in the nuclear power industry and in the making of super-alloys. Its low absorption of neutrons makes it an invaluable material in many industries.
Is there a 140th element?
The periodic table of elements is composed of 118 known elements. But have you ever heard of the 140th element? Unquadnilium, also known as eka-thorium or element 140, is the temporary name of a superheavy element on the periodic table in the superactinide series that has the temporary symbol Uqn and has the atomic number 140. In the periodic table of elements, it is a f-block element.
What is Unquadnilium?
Unquadnilium is a theoretical element that was first proposed in 1999 by Russian scientists. It has yet to be synthesized and is currently only a theoretical element. Unquadnilium is an element in the superactinide series, which is part of the f-block elements in the periodic table. This element is located below actinium and above dubnium in the periodic table.
Is Unquadnilium real?
As of 2012, no attempt has been made to synthesize unquadnilium. Currently, unquadnilium goes under a systematic temporary element name. This element has not been observed in nature and has not been synthesized in a laboratory. It is not known whether it is possible to synthesize unquadnilium or even if it exists.
What is the 130th element?
The 130th element is Cesium. It is a metallic element that is soft, silvery-white and highly reactive. Cesium is a member of the alkali metal group and has the symbol Cs and the atomic number 55. Cesium is found in nature in the form of several isotopes, with the most common being cesium-133, which has a half-life of 2.3 years.
What is the newest element?
The newest element is Nihonium, which has the symbol Nh and the atomic number 113. It was discovered in 2004 by a team of Japanese scientists and is one of the six elements in the seventh period of the periodic table. Nihonium is a synthetic element and is not found in nature.
What will be the last element?
It is not known what the last element will be, as new elements are constantly being discovered and synthesized. Scientists are currently working on synthesizing elements beyond the current 118, such as unquadnilium and untrioctium, but it is not known if these elements will be the last ones ever discovered.
What’s the rarest element ever?
The rarest element ever is astatine, which has the symbol At and the atomic number 85. It is the rarest naturally occurring element in the Earth’s crust, occurring only as the decay product of various heavier elements. All of astatine’s isotopes are short-lived; the most stable is astatine-210, with a half-life of 8.1 hours.
Is element 138 possible?
Element 138, also known as untrioctium, is an unsynthesized element with the symbol Uto and atomic number 138. This element has yet to be synthesized and is currently only a theoretical element. It is not known if it is possible to synthesize untrioctium, or even if it exists.
Is element 125 possible?
Element 125, also known as unbihexium, is a theoretical element that has yet to be synthesized. It has the symbol Ubh and atomic number 125, and is part of the f-block elements in the periodic table. It is not known if it is possible to synthesize unbihexium or even if it exists.
The periodic table is constantly evolving, with new elements being discovered and synthesized. While some elements, such as unquadnilium, remain theoretical, others, such as nihonium, have been discovered and synthesized in laboratories. It is not known what the last element will be, but scientists are constantly working on discovering and synthesizing new elements.
Is polonium 212 an isotope?
Polonium (Po) is a rare, naturally occurring element that has many isotopes and isomers. These isotopes and isomers have atomic masses ranging from 188u to 220u, and all are radioactive. The most widely available isotope is 210Po, which has a half-life of 138.376 days. This makes it the longest-lived naturally occurring polonium isotope.
Other Properties of Polonium
Most of the polonium isotopes have very short half-lives, but some are stable for much longer periods of time. 209Po, for example, has a half-life of 125.2 years, making it the longest-lived of all polonium isotopes. It can be created through the alpha, proton, or deuteron bombardment of bismuth or lead in a cyclotron.
In addition to its isotopes, polonium also has 33 isomers. Isomers are atoms of the same element with different structures. Isomers of polonium range in atomic mass from 188u to 220u. Most of these isomers are unstable, but a few are long-lived.
Is Polonium 212 an Isotope?
The answer is yes. Polonium 212 is an isotope of the element polonium. It has an atomic mass of 212u and a half-life of approximately 0.00000002 seconds. This makes it one of the shortest-lived naturally occurring isotopes of polonium.
Polonium 212 is part of a decay chain that begins with uranium-238 and ends with lead-206. This decay chain is known as the uranium-radium-actinium series. Polonium-212 is the sixth element in this decay chain, and is followed by bismuth-212 and then lead-208.
In conclusion, polonium 212 is an isotope of the element polonium. It has an atomic mass of 212u and a half-life of approximately 0.00000002 seconds. Polonium 212 is part of the uranium-radium-actinium decay series, and is followed by bismuth-212 and then lead-208. Polonium 212 is one of the shortest-lived naturally occurring isotopes of polonium.



Leave a Comment