Atoms have long been a source of fascination for scientists and laypeople alike. They are the building blocks of all matter, and understanding how they work is fundamental to understanding the universe we live in. But what exactly are atoms? And what makes them unique?
Atoms are the smallest units of matter that can exist on their own. They consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and together, these particles make up an atom. Protons are positively charged particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are uncharged particles that inhabit the nucleus of an atom, and together with protons, form the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom.
Each atom is unique in that it has a certain number of protons, electrons, and neutrons. The number of protons determines the element of the atom, and the number of electrons and neutrons determine the isotope. For example, an atom with 28 protons, 28 electrons, and 30 neutrons is an isotope of silicon.
But what has 32 neutrons and 28 electrons? This combination of particles is found in a particular element, one that has been the subject of much study and debate: the hydrogen atom. Hydrogen atoms have just one proton, one electron, and 32 neutrons. This combination of particles is what makes hydrogen atoms so special. Hydrogen atoms are the simplest atoms, and the only element with just one proton and one electron.
Hydrogen atoms are so important because of how they interact with other atoms. Their single electron allows them to form bonds with other atoms, and this makes them essential for many chemical reactions. Hydrogen atoms are also the lightest atoms, and this allows them to move quickly between molecules, making them important for energy.
Hydrogen is also important for life. It is the most abundant element in the universe and is essential for life to exist. It forms the basis of water, and is a key component of all living organisms.
Hydrogen atoms have 32 neutrons and 28 electrons, and this combination of particles makes them special. They are the basis of life, essential for many chemical reactions, and incredibly important for the universe. Understanding their properties and reactions is an essential part of understanding the world around us.
What has 32 neutrons and 28 electrons?
Atoms are comprised of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Each of these particles has a distinct role in the structure of atoms, and it is important to understand the characteristics of each one. In particular, the neutron and proton are important components of the nucleus of an atom, while electrons are found in the surrounding shells. So, what has 32 neutrons and 28 electrons? The answer is a neutral atom of Nickel (Ni).
Neutrons
Neutrons are uncharged particles that have a mass of 1.67493 x 10-27 kg, which is slightly greater than the mass of a proton but nearly 1839 times greater than the mass of an electron. Neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom along with protons and they are held together by the strong nuclear force. The mean square radius of a neutron is about 0.8 x 10-15 m or 0.8 fm and they are spin-½ fermions.
Protons
Protons are positively charged particles with a mass of 1.67262 x 10-27 kg, which is slightly lighter than the mass of a neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than the mass of an electron. Protons are found in the nucleus of an atom, along with neutrons, and they are held together by the strong nuclear force. The mean square radius of a proton is about 0.87 x 10-15 m or 0.87 fm and they are spin-½ fermions.
Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged particles that have a very small mass compared to protons and neutrons. They have a mass of 9.10938356 x 10-31 kg and are found in the shells surrounding the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are held in place by the electromagnetic force and they are spin-½ fermions.
Nickel (Ni)
Nickel (Ni) is a neutral atom that has a total of 28 electrons and 32 neutrons. The 28 electrons are arranged in the following configuration: 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2. The 32 neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom along with 28 protons. Nickel (Ni) is a transition metal and it has many uses in industry, such as in the production of coins and jewelry.
In conclusion, Nickel (Ni) is an atom that has 32 neutrons and 28 electrons. Neutrons are uncharged particles with a mass of 1.67493 x 10-27 kg, while protons are positively charged particles with a mass of 1.67262 x 10-27 kg. Electrons are negatively charged particles with a mass of 9.10938356 x 10-31 kg and are found in the shells surrounding the nucleus of an atom. Nickel (Ni) is a transition metal that has many uses in industry.
What has 28 protons and 33 neutrons?
The answer to this question is Iron, or Fe. Iron is an element in the periodic table, and it has an atomic number of 26 and a mass number of 56. This means that it has 28 protons and 33 neutrons.
Iron is one of the most abundant elements in the universe, and it’s found in many different forms in nature. In its purest form, it is a silver-gray metal with a shiny surface. It is also incredibly durable, making it a popular choice for use in a variety of applications.
What are the Properties of Iron?
Iron is an extremely strong metal, and it has a melting point of 1,535°C. It is also very malleable, meaning it can be shaped into different forms without breaking. In addition, it is highly conductive, making it a great choice for use in electrical components.
Iron also has a number of other properties that make it a useful element. It is relatively corrosion-resistant, meaning it can survive in harsh conditions without degrading. It is also resistant to heat, making it a good choice for use in high-temperature applications.
What is the Role of Neutrons in Iron?
Neutrons play an important role in the structure of iron. They are found in the nucleus of the atom, and they are responsible for balancing out the positive charge of the protons. This helps to create a stable nucleus that is not easily disturbed.
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is also important in determining the type of element it is. Iron has 28 protons and 33 neutrons, which makes it a stable element. If the number of neutrons were to change, it could alter the properties of the element, which could have a significant impact on its uses.
What are the Uses of Iron?
Iron is used in a variety of different applications, from construction to industry. It is a popular choice for use in buildings and bridges due to its strength and durability. It is also used to make tools and machinery, as well as medical equipment.
Iron is also used in the production of steel, which is one of the most widely used materials in the world. Steel is incredibly strong and durable, making it a popular choice for use in a variety of applications, from buildings to automobiles.
Iron is an incredibly versatile element, and it has a number of different uses. It has 28 protons and 33 neutrons, which gives it a stable nucleus and a range of properties that make it a great choice for use in a variety of applications. From construction to industry, iron is an essential part of our lives.
What has 28 protons and 32 neutrons?
The answer to this question is an atom. Atoms are the smallest particles of matter that make up all physical objects. They are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The number of protons in an atom determines its identity, while the number of neutrons can vary.
Atoms with 28 protons and 32 neutrons are part of a larger group of atoms known as isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is known as its mass number.
Atoms with 28 protons and 32 neutrons have a mass number of 60 and are known as Cobalt-60 ((^{60}_{27}ce{Co})). This isotope is used in medicine for radiation therapy, as it emits gamma radiation. It is also used in industrial radiography and in nuclear power plants.
Atoms with 24 protons and 11 neutrons have a mass number of 35 and are known as Sodium-24 ((^{24}_{11}ce{Na})). This isotope is used in medical imaging and radiation therapy, as well as for industrial radiography. It is also used in research to study the properties of elements.
Atoms with 20 protons and 25 neutrons have a mass number of 45 and are known as Calcium-45 ((^{45}_{20}ce{Ca})). This isotope is used in medical imaging and radiation therapy, as well as in research. It is also used to study the properties of elements and to monitor nuclear reactors.
Atoms with 38 protons and 52 neutrons have a mass number of 90 and are known as Strontium-90 ((^{90}_{38}ce{Sr})). This isotope is used in medical imaging and radiation therapy, as well as in research to study the properties of elements. It is also used to monitor nuclear reactors.
How Many Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons are in Each Atom?
The number of protons in an atom is always the same for a given element. However, the number of electrons and neutrons can vary depending on the isotope.
For example, the atom of Cobalt-60 has 27 protons, 27 electrons, and 33 neutrons. The atom of Sodium-24 has 11 protons, 11 electrons, and 13 neutrons. The atom of Calcium-45 has 20 protons, 20 electrons, and 25 neutrons. And the atom of Strontium-90 has 38 protons, 38 electrons, and 52 neutrons.
What is a Neutron?
A neutron is a subatomic particle with no electric charge and a rest mass equal to 1.67493 × 10−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but nearly 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a mean square radius of about 0.8×10−15 m, or 0.8 fm, and it is a spin-½ fermion.
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other through the nuclear force, while protons repel each other via the electric force due to their positive charge.
Atoms with 28 protons and 32 neutrons are part of a larger group of atoms known as isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is known as its mass number.
The number of protons in an atom is always the same for a given element. However, the number of electrons and neutrons can vary depending on the isotope. Neutrons are subatomic particles with no electric charge and a rest mass greater than that of the proton but nearly 1839 times greater than that of the electron. They are responsible for the attraction between protons and neutrons that forms the atomic nucleus.
What atom has 28 protons 28 electrons and 30 neutrons?
Atoms are made up of three particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The number of protons and electrons in an atom determines its identity, while the number of neutrons can vary from one atom to another. The atom with 28 protons, 28 electrons, and 30 neutrons is the Nickel-60 (60Ni) isotope.
Atomic Structure
Atoms are composed of a nucleus and electrons that orbit around it. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons, while the electrons have very small masses compared to protons and possess a negative charge. In addition to protons, the nucleus of an atom contains neutrons. Neutrons possess no charge and have a mass very similar to that of protons.
Proton Characteristics
The proton has a positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to 1.67262 x 10-27 kg (938.272 MeV/c2)—marginally lighter than that of the neutron but nearly 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean square radius of about 0.87 x 10-15 m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
Neutron Characteristics
The neutron has no electric charge and a rest mass equal to 1.67493 x 10-27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but nearly 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a mean square radius of about 0.8 x 10-15 m, or 0.8 fm, and it is a spin-½ fermion.
Atomic Nucleus
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other through the nuclear force, while protons repel each other via the electric force due to their positive charge. The number of protons and electrons in an atom determines its identity, while the number of neutrons can vary from one atom to another.
Nickel-60 (60Ni) Isotope
The Nickel-60 (60Ni) isotope is an atom with 28 protons, 28 electrons, and 30 neutrons. This isotope is the most abundant isotope of nickel, accounting for nearly 68% of the element’s total mass. It is a stable isotope, meaning that it is not radioactive.
Uses of Nickel-60 Isotope
Nickel-60 has many applications, including the production of medical isotopes for diagnosing and treating illnesses, and the production of gamma rays for radiation therapy. It is also used in the production of nuclear weapons and in certain types of research.
Atoms are composed of a nucleus and electrons that orbit around it. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons, while the electrons have very small masses compared to protons and possess a negative charge. The Nickel-60 (60Ni) isotope is an atom with 28 protons, 28 electrons, and 30 neutrons. This isotope is the most abundant isotope of nickel, accounting for nearly 68% of the element’s total mass and has many applications, including the production of medical isotopes for diagnosing and treating illnesses, and the production of gamma rays for radiation therapy.
What element has 28 protons 28 electrons and 30 neutrons?
Atoms are made up of various components, such as protons, electrons, and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge and have a mass of 1 amu (atomic mass units). Electrons have very small masses compared to protons, and possess a negative charge. In addition to protons, the nucleus of an atom contains neutrons. Neutrons possess no charge and have a mass very similar to that of protons.
The number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom determine its identity. For an atom to be neutral, the number of protons must equal the number of electrons. The number of neutrons in an atom, however, can vary. Unlike protons, whose number controls an atom’s identity, atoms of the same identity can have a different number of neutrons within the nucleus. This is known as an isotope.
Exercise (PageIndex{1}) asked for the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in three different isotopes: 199F1–, 5224Cr3+, and 3115P3–. The answers are 9 protons, 10 neutrons, 10 electrons for 199F1–; 24 protons, 28 neutrons, 21 electrons for 5224Cr3+; and 15 protons, 16 neutrons, 18 electrons for 3115P3–.
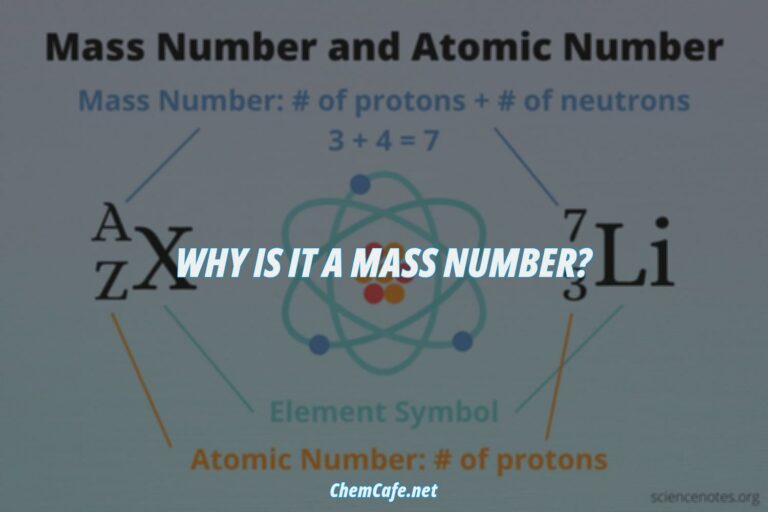
Mass Number and Charge Number
Now that we know the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each isotope, we can determine the mass number and charge number of each isotope. The mass number of an isotope is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For example, the mass number of 199F1– is 19, since it has 9 protons and 10 neutrons. The charge number of an isotope is equal to the number of protons minus the number of electrons. For example, the charge number of 199F1– is -1, since it has 9 protons and 10 electrons.
Atomic Number and Element Identity
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. For example, the atomic number of Fluorine is 9, since it has 9 protons in its nucleus. The identity of an element is determined by its atomic number. For example, an element with an atomic number of 9 is Fluorine.
In conclusion, an element with 28 protons, 28 electrons, and 30 neutrons is an isotope of Chromium with a mass number of 52 and a charge number of +3. Its atomic number is 24, and its identity is Chromium.
Atoms are fascinating and complex structures that provide insight into the building blocks of our universe. By understanding the components of an atom, such as protons, neutrons, and electrons, and how they relate to each other, we can gain a better understanding of the world around us.
What element has 28 protons and 28 electrons?
Atoms are the building blocks of matter and consist of three main particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons have very small masses compared to neutrons, and possess opposite charges. Protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge.
The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, and each element has its own unique atom that contains a specific number of protons. Furthermore, each atom also has the same number of electrons as protons. This means that if an atom has 28 protons, it also has 28 electrons.
What is an Isotope?
An isotope is an atom of the same element that has a different number of neutrons. Neutrons possess no charge and have a mass very similar to that of protons. This means that an atom can have the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons.
For example, an atom of hydrogen has one proton and one electron, and is known as hydrogen-1. However, there is also an isotope of hydrogen called hydrogen-2, which has one proton and one electron, but two neutrons.
The Building Blocks of Atoms
Atoms are made up of even smaller particles such as quarks, muons, gluons, and many others with exotic names and properties. Quarks are the smallest of these particles, and are held together by gluons. Protons and neutrons are made up of quarks, and each quark has its own charge.
Muons, on the other hand, are subatomic particles with no charge and a mass similar to that of the electron. They are formed when high-energy cosmic rays interact with the Earth’s atmosphere, and can be found in the upper atmosphere.
In conclusion, an atom with 28 protons and 28 electrons is an element with an atomic number of 28. This element can also have different numbers of neutrons, resulting in isotopes of the same element. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles such as quarks, muons, and gluons, which have their own charges and masses.



Leave a Comment