The word ‘neutron’ is one of the most important and fundamental components of modern day physics. It is an essential building block of matter, and its discovery and understanding has been instrumental in the development of our current understanding of the universe. But what exactly is a neutron, and why is it so important?
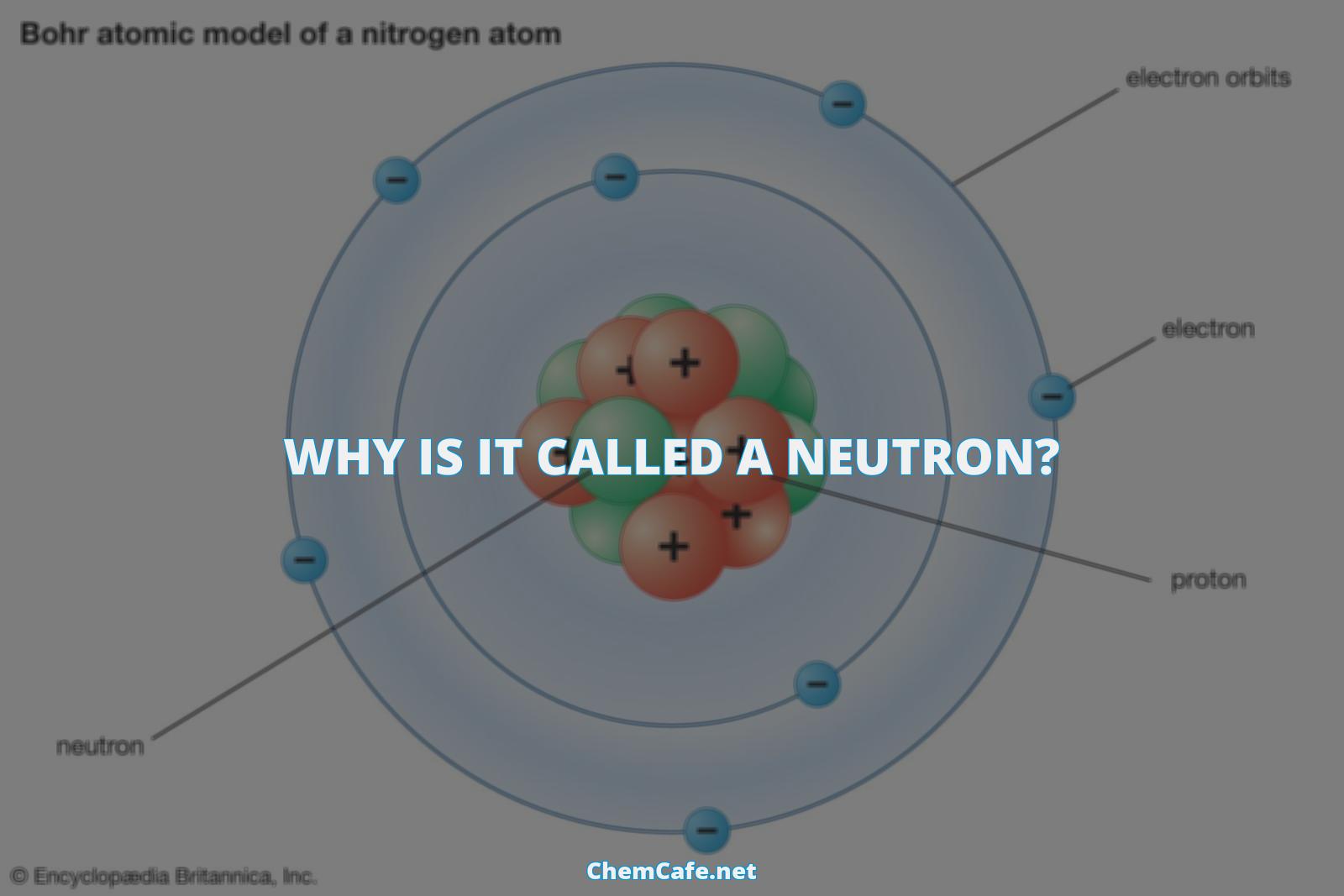
A neutron is a subatomic particle that carries no electric charge, and is one of the basic pieces of matter that makes up the atoms in our world. It has been attributed to Rutherford by Glasson1 and to W. D. Harkins2 by Glasstone3, and is thought to have been used by neither Rutherford or Hawkins before about 1920. Neutrons are composed of two down quarks and one up quark, each with 1/3 and 2/3 elementary charge respectively, and are located in the nucleus of an atom.
The discovery of the neutron was a monumental breakthrough in our understanding of the universe and has had significant implications in the fields of physics, chemistry, and biology. It can be used to explain the stability of certain isotopes, which can be used in nuclear power and medical treatments such as cancer therapy. It is also a key ingredient in the creation of new elements, and can be used to explain the abundance of elements in the universe. The neutron has also played an important role in the development of quantum mechanics and particle physics.
The importance of the neutron cannot be overstated, however its name is still a mystery and it is unclear how it received its designation. Most likely it was named after Rutherford or Hawkins, but it is also possible that it was given its name based on its neutral charge. Regardless of its origin, it is clear that the neutron is an integral part of our understanding of the universe and will continue to be for years to come.
Why is it called a neutron?
The neutron is one of the most fundamental particles in the universe, and it’s been studied for centuries. But why is it called a neutron? This article will explore the history of the neutron and explain why it was given its unique name.
History of the Neutron
The word ‘neutron’ was first used in the early 1920s by physicist Ernest Rutherford. He used the term to refer to a hypothetical combination of a hydrogen nucleus (also known as a ‘positive electron’ or ‘proton’) and an ordinary negative electron. Rutherford’s idea of a neutron eventually led to the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power.
In the 1950s, physicists realized that the neutron was made up of even smaller particles called quarks. These quarks are held together by a force called the strong nuclear force. The strong nuclear force is responsible for binding together protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Why Was It Called a Neutron?
The name ‘neutron’ was originally chosen because it describes the particle’s basic properties. Neutrons are electrically neutral, meaning they have no charge. This property makes them different from protons and electrons, which have positive and negative charges, respectively.
The word ‘neutron’ is derived from the Latin words neutrum and tonus, which mean ‘neutral tone’. This reflects the fact that the neutron has no charge.
The Role of the Neutron
Neutrons play a key role in the structure of atoms. In a typical atom, the number of protons and electrons is equal, resulting in a neutral charge. But in certain atoms, the number of protons and electrons is not equal. In these cases, the atom is said to be ‘ionized’, meaning it has a positive or negative charge.
In order to neutralize the charge of an ionized atom, neutrons are added to the nucleus. This process is called ‘neutron capture’. Neutron capture is an important part of nuclear reactions, such as those that take place in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.
The neutron is an essential part of the universe, and it’s been studied for centuries. Its name comes from the Latin words neutrum and tonus, which mean ‘neutral tone’. This reflects the fact that the neutron has no charge. Neutrons play a key role in the structure of atoms, and they are essential for nuclear reactions, such as those that take place in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.
What do you mean by neutrons?
Neutrons are subatomic particles located in the nucleus of every atom, except atoms of hydrogen. They possess a mass similar to protons and have a neutral electrochemical charge of zero. Elements are primarily identified by their atomic number, which correlates to the number of protons they possess.
A Brief History of Neutrons
Neutrons were first discovered in 1932 by British physicist James Chadwick. Chadwick was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1935 for his discovery. He found that when bombarded with alpha particles, beryllium emitted radiation composed of particles with no electric charge and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Chadwick named these particles neutrons.
Neutron Properties
The most important property of a neutron is its mass. A neutron has a mass of 1.675 x 10-27 kg, which is slightly more than the mass of a proton. Neutrons also have a neutral electric charge, meaning they are neither positively nor negatively charged. This makes them very stable and prevents them from interacting with other particles or fields.
Neutron Characteristics
Neutrons are an essential part of atoms, as they provide the stability of the nucleus. The number of neutrons in an atom is called the neutron number, and is usually represented by the letter ‘N’. This number is usually the same as the number of protons in the nucleus, but in some cases, the number of neutrons can be greater or less than the number of protons.
Neutron Uses
Neutrons are used in a variety of ways, including in nuclear power plants, medical imaging and research, and material science. In nuclear power plants, neutrons are used to initiate the process of nuclear fission, which is the splitting of atoms to release energy. In medical imaging, neutrons are used to create images of the human body, such as MRI scans. In research, neutrons are used to study the structure of molecules and atoms. Finally, in material science, neutrons are used to study the properties of materials, such as their strength and durability.
Neutrons are an essential part of atoms, as they provide the stability of the nucleus. They possess a mass similar to protons and have a neutral electrochemical charge of zero. Neutrons are used in a variety of ways, including in nuclear power plants, medical imaging and research, and material science. Understanding neutrons is essential to furthering our knowledge of the universe and how it works.
Why are neutrons called neutral?
The neutron is an elementary particle located in the nucleus of every atom, except atoms of hydrogen. It has a mass similar to that of a proton and a neutral electrochemical charge of zero. Neutrons are an important component of atomic structure and are primarily identified by their atomic number, which correlates to the number of protons they possess.
What is a Neutron?
A neutron is a subatomic particle that has no electrical charge and is found in the nucleus of all atoms, except hydrogen. It has a mass that is slightly larger than that of a proton and is held together by strong nuclear forces. A neutron also has about the same diameter as a proton, or (1.7 times 10^{-15}) meters. As you might have already guessed from its name, the neutron is neutral. In other words, it has no charge whatsoever and is therefore neither attracted to nor repelled from other objects. Neutrons are in every atom (with one exception), and they are bound together with other neutrons and protons in the atomic nucleus.
Why are Neutrons Called Neutral?
The name “neutron” is derived from the Latin word “neutrum”, which means “neutral”. This is because the neutron has no electric charge. It is neither positive nor negative, and thus has no effect on the electric field around it.
The Role of Neutrons in Atomic Structure
Neutrons are essential for understanding the structure of atoms and how they interact with each other. Since they have no electrical charge, they do not interact with other atoms in the same way that protons and electrons do. Instead, they act as a stabilizing force in the nucleus, keeping the protons from repelling each other and allowing the nucleus to remain stable. This is why neutrons are so important in atomic structure and why they are so essential for understanding the behavior of atoms.
The Significance of Neutrons
Neutrons are a critical component of atomic structure and play a major role in understanding the behavior of atoms. They are also important for understanding the nature of matter and how different elements interact with each other. Without them, it would be virtually impossible to understand the structure of atoms and the properties of matter.
In conclusion, neutrons are called neutral because they have no electric charge. They are essential for understanding the structure of atoms and how they interact with each other. They also play a key role in understanding the behavior of atoms and the nature of matter.
How neutrons are in an atom?
Atoms are made up of three key particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. While protons and electrons have a charge, neutrons are neutral, meaning they have no charge at all. In ordinary hydrogen, the nucleus contains just one proton, while in all other atoms the nucleus contains both protons and neutrons. Neutrons are an important part of the atom, and they play an integral role in the structure and stability of the atom.
Atoms are made up of a nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, which are bound together by the strong nuclear force. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element, while the number of neutrons determines the isotope of that element.
The number of neutrons in an atom can vary. If the number of neutrons is the same as the number of protons, the atom is said to be stable. But if the number of neutrons is greater or lesser than the number of protons, the atom is said to be unstable. Unstable atoms are known as isotopes, and they are often radioactive, meaning they can emit radiation.
The Mass of Neutrons
If an electron was the mass of a penny, a proton or a neutron would have the mass of a large bowling ball! Neutrons have a neutral electric charge (neither negative nor positive) and have slightly more mass than positively charged protons. They have a rest mass equal to 1.67492749804 × 10−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton but 1,838.68 times greater than that of the electron.
The Role of Neutrons
Neutrons are an important part of the atom, and they play an integral role in the structure and stability of the atom. Neutrons and protons, commonly called nucleons, are bound together in the dense inner core of an atom, the nucleus, where they account for 99.9 percent of the atom’s mass. Neutrons are also important for research in medicine, materials, and other fields. They are used to create new materials such as superconductors, to diagnose cancer using neutron imaging, and to study the structure of matter.
Free Neutrons
In addition to being found in the nucleus of atoms, neutrons can also exist outside of the nucleus. These “free” neutrons are produced by nuclear fission and fusion processes. Free neutrons can also be used to power nuclear reactors, which are an important source of energy in many parts of the world.
Overall, neutrons are an essential part of the atom. They are neutral particles that have a slightly larger mass than protons, and they are responsible for the structure and stability of the atom. In addition to being found in the nucleus of atoms, neutrons can also exist outside of the nucleus, and they are used for a variety of applications, from creating new materials to powering nuclear reactors.
What nucleus has no electrical charge?
Atoms are composed of three types of particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons. The nucleus is the central part of an atom, and it contains most of its mass. The nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and neutrons. The protons have a positive charge, and the neutrons have no electrical charge. But what nucleus has no electrical charge?
The answer is that some nuclei have no electrical charge, and these are known as “neutral nuclei.” Neutral nuclei are found in certain isotopes of certain elements, such as hydrogen and helium. The most common neutral nucleus is the neutron. Neutrons are uncharged particles that have a mass roughly equal to the mass of a proton.
Neutrons are an important part of the nucleus of an atom because they give the nucleus stability. Without neutrons, protons, which have the same charge, would repel each other and the nucleus would quickly break apart. By adding neutrons to the nucleus, the protons are held together in a stable configuration. This is why the nucleus of an atom is often referred to as a “nuclear lattice.”
Neutrons and Nuclear Forces
Neutrons also play an important role in the binding of the nucleus. Neutrons interact with protons through the strong nuclear force. This force is many times stronger than the electromagnetic force, which holds electrons in their shells around the nucleus. The strong nuclear force is responsible for holding the nucleus together, and it is due to this force that the nucleus is stable and does not break apart.
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is usually equal to the number of protons. This is because the strong nuclear force between the protons and neutrons is the same for both particles. If the number of neutrons is greater than the number of protons, the nucleus is said to be “neutron-rich” and if the number of protons is greater than the number of neutrons, the nucleus is said to be “neutron-poor.”
Neutron-Rich and Neutron-Poor Nuclei
Neutron-rich nuclei are unstable and tend to undergo radioactive decay. This is because the nucleus is held together by the strong nuclear force, and the extra neutrons add energy to the nucleus and destabilize it. Neutron-poor nuclei, on the other hand, are more stable and tend to remain intact.
Neutron-rich nuclei are important in the formation of elements heavier than helium. This is because, when a neutron-rich nucleus undergoes radioactive decay, it usually emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and becomes a nucleus of an element with an atomic number one less than the original nucleus. This process is known as alpha decay and is responsible for the formation of heavier elements.
Neutron-poor nuclei are also important in the formation of elements heavier than helium. This is because, when a neutron-poor nucleus undergoes radioactive decay, it often emits a beta particle (electron) and becomes a nucleus of an element with an atomic number one greater than the original nucleus. This process is known as beta decay and is responsible for the formation of heavier elements.
In conclusion, some nuclei have no electrical charge and these are known as neutral nuclei. The most common neutral nucleus is the neutron. Neutrons are important for the stability of the nucleus, as well as for the formation of elements heavier than helium. Neutron-rich nuclei are unstable and tend to undergo radioactive decay, while neutron-poor nuclei are more stable and tend to remain intact.
Where are neutrons located in an atom?
Neutrons are a subatomic particle located within the nucleus of an atom, with protons making up the majority of its mass. Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, the neutron was the first subatomic particle found to have no electric charge. The number of neutrons inside the nucleus is called the neutron number, which can be determined by subtracting the proton number from the atomic mass number.
What is a neutron?
A neutron is a neutrally charged particle made up of one up quark and two down quarks. It has a mass of slightly more than a proton and is found in the nucleus of all atoms, except for hydrogen. In beta decay, a neutron can transform into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. Along with protons, neutrons are also known as nucleons, and they make up nearly the entire mass of an atom.
What are free neutrons?
Free neutrons are those that are no longer confined to the nucleus of an atom. They are produced through nuclear fission and fusion processes, and they are used in research in medicine, materials, and other fields. Neutrons can also be used to study the structure of atoms, molecules, and materials.
What are the different types of neutrons?
The two main types of neutrons are thermal neutrons and fast neutrons. Thermal neutrons move slowly and are easily absorbed by other atoms, while fast neutrons have a higher energy and can penetrate matter more easily. Neutrons can also be classified according to their energy, with low energy neutrons being slow and easily absorbed, and high energy neutrons being fast and penetrating.
What is neutron scattering?
Neutron scattering is a technique used to study the structure of atoms, molecules, and materials. It involves firing a beam of neutrons at a sample material and measuring how the neutrons interact with the atoms in the material. By measuring the intensity and direction of the scattered neutrons, researchers can gain insight into the structure of the material.
Neutrons are an essential tool for studying the structure of matter and can be used to study a variety of materials, from metals and alloys to proteins and viruses. They are also used in applications such as medical imaging, nuclear reactors, and nuclear weapons. By understanding where neutrons are located in an atom, scientists can gain a better understanding of the structure of matter and how it behaves.



Leave a Comment