How Many Electrons Does Nitrogen Have?
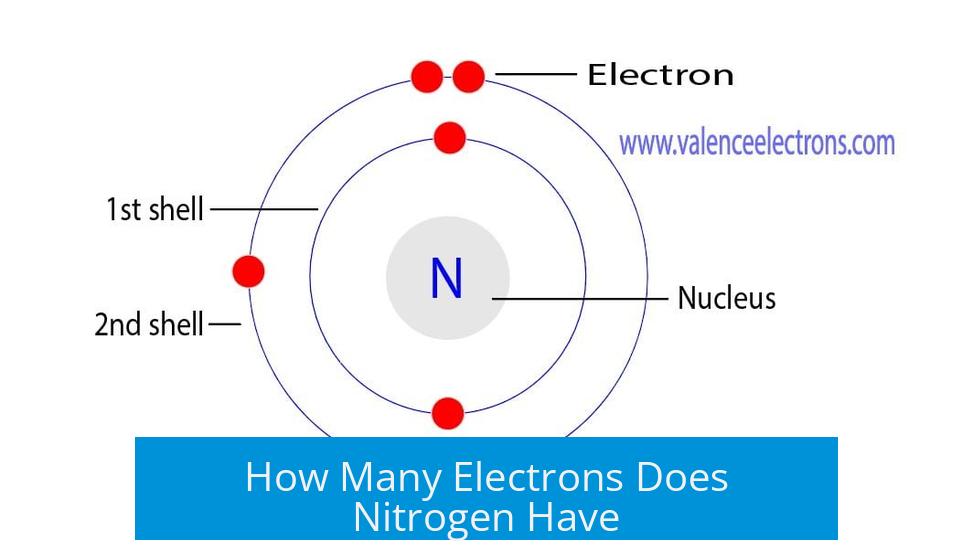
Nitrogen has 7 total electrons, which equals its atomic number. Of these, 5 electrons are valence electrons in the outermost shell.
Understanding Atomic Number and Electron Count

The atomic number defines the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Since nitrogen’s atomic number is 7, it has 7 electrons orbiting its nucleus.
Atoms maintain electrical neutrality. The positive charge from 7 protons balances the 7 negative charges from electrons. This balance keeps nitrogen stable as a neutral atom.
In summary:
- Atomic number of nitrogen = 7
- Number of protons = 7
- Number of electrons in a neutral atom = 7
Valence Electrons vs Total Electrons
Electrons occupy energy levels or shells around the nucleus. The electrons in the outermost shell are called valence electrons. These govern chemical behavior and bonding.
Nitrogen’s electrons arrange as follows:
- First shell: 2 electrons (maximum capacity for first shell)
- Second shell: 5 electrons (valence shell)
Thus, nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and 7 total electrons. This distinction clarifies common misunderstandings.
Why Valence Electrons Matter
Valence electrons determine how nitrogen interacts chemically. The 5 outer electrons can be shared or transferred to form bonds. For example, in ammonia (NH3), nitrogen shares its valence electrons.
Understanding valence electrons is essential for predicting nitrogen’s role in chemical reactions, molecular structures, and bonding patterns.
Common Confusions and Misconceptions
People often confuse total electrons with valence electrons. Since valence electrons are key for chemistry, sometimes the number 5 (valence electrons) is mistakenly identified as the total electrons.
Others might mistake nitrogen ions for neutral atoms. For example:
- N2+ nitrogen ion has fewer electrons due to positive charge
- Neutral nitrogen atom always has 7 electrons
This can lead to incorrect answers about nitrogen’s electron count.
Additionally, the distinction between an atom (micro world) and molecular nitrogen (N2 gas) is important. The atom “N” refers to a single nitrogen atom with 7 electrons, not the nitrogen gas molecule, which contains two nitrogen atoms joined together.
Electron Configuration of Nitrogen
The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2p3. It breaks down as follows:
| Shell/Subshell | Electrons | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1s | 2 | Core electrons, inner shell |
| 2s | 2 | Valence shell, lower energy |
| 2p | 3 | Valence shell, higher energy |
This configuration accounts for all 7 electrons, with 5 in the valence shell (2s and 2p subshells combined).
Significance in the Periodic Table
Nitrogen resides in Group 15 of the periodic table. Elements in this group share similar valence electron counts, all having 5 valence electrons. This imparts characteristic chemical properties.
For nitrogen, this means it typically forms three bonds to satisfy its octet rule — by sharing three of its valence electrons with other atoms.
Summary and Key Points
- Nitrogen has 7 electrons in total. This matches its atomic number of 7.
- Out of the 7 electrons, 5 are valence electrons located in the outermost electron shell (second shell).
- Valence electrons determine nitrogen’s chemical behavior and bonding capability.
- Confusion arises when valence electrons are mistaken for total electrons.
- The electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p3 reflects its full electron arrangement.
- In macroscopic form, nitrogen gas (N2) consists of two nitrogen atoms bonded together.




Leave a Comment